Figure 7. Depletion of CoRL exacerbates kidney fibrosis and impairs recovery during pUUO:
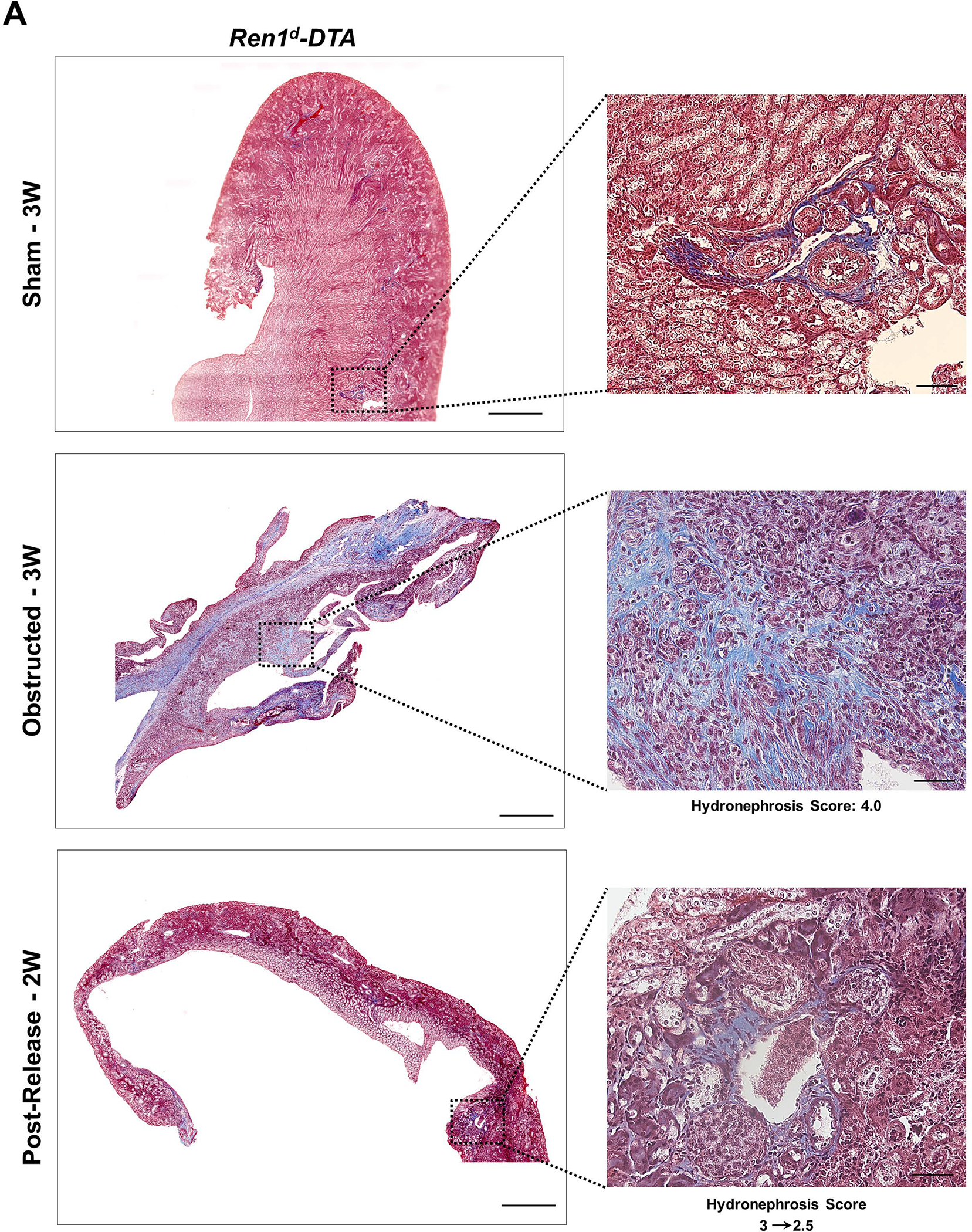
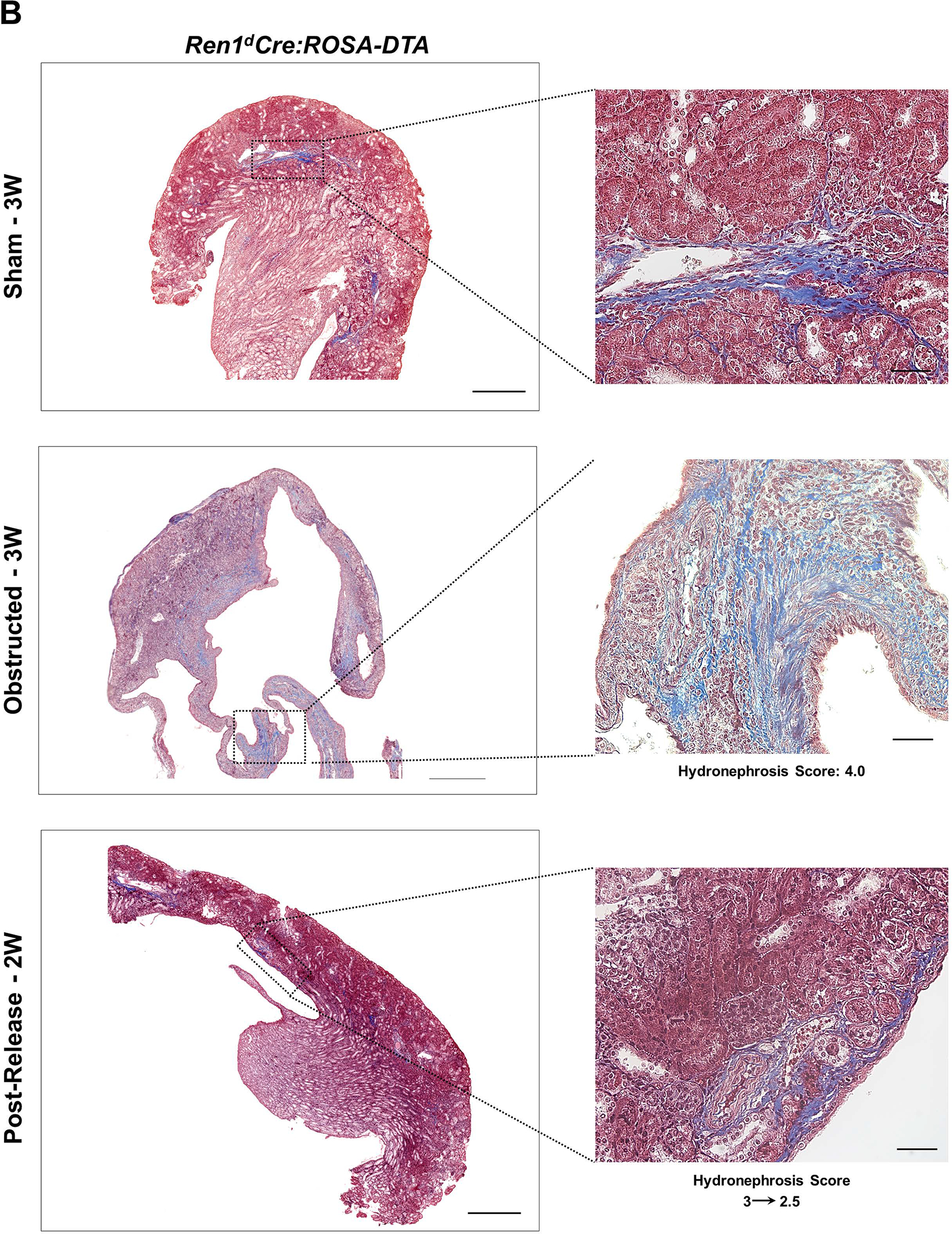
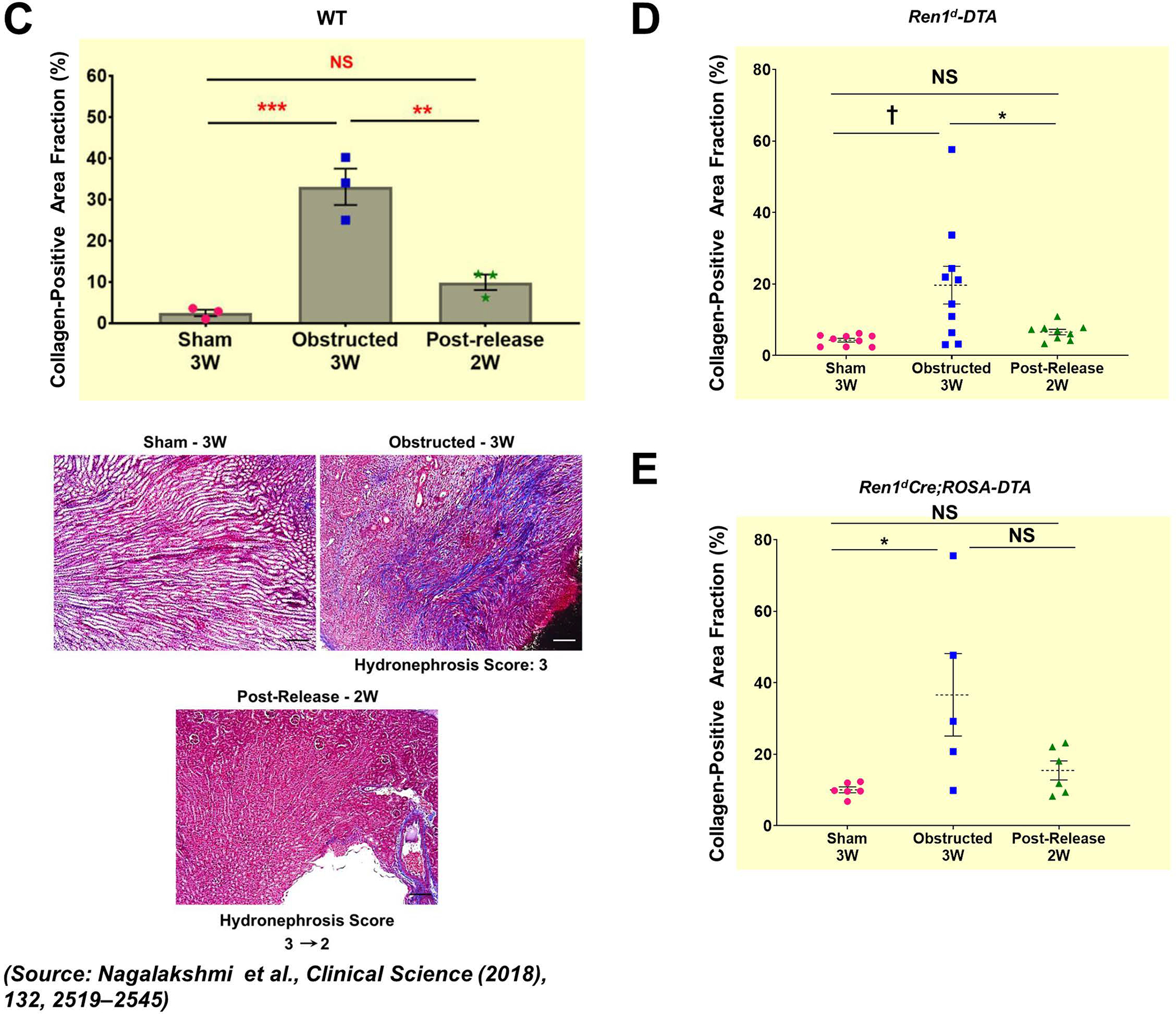
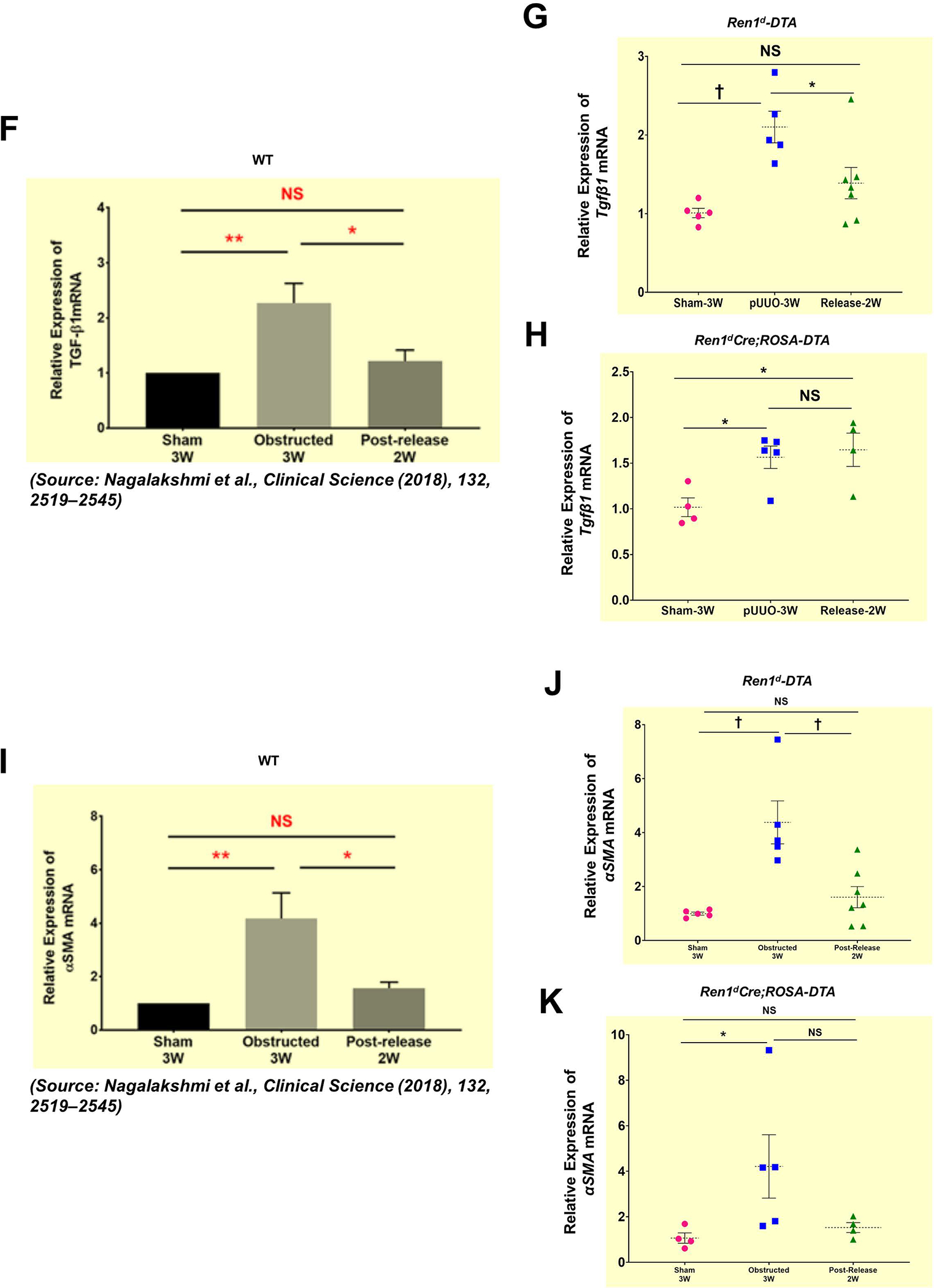
(A-B) Representative tile scan images on the left and enlarged view on the right show Masson’s Trichrome staining on the kidneys from various surgery treatments. Exacerbated collagen deposition occurs in the persistently obstructed kidneys. In addition, depletion of CoRL in Ren1dCre;ROSA-DTA animals leads to a poor recovery from the fibrotic damage following the relief of obstruction (Scale bar 500μm, 50μm) (C-E) Quantification of the collagen-positive, fibrotic area fractions in the kidneys confirmed a significant increase post-obstruction in both DTA models similar to the WT mice with no toxin expression. Following the removal of obstruction the fibrotic areas decreased significantly in the WT and Ren1d-DTA goup. In Ren1dCre;ROSA-DTA animals, the collagen-positive area was lower, although did not reach statistical significance after the relief of obstruction compared to the persistently obstructed kidneys (F-H) Tgfb1 mRNA measured by qRT-PCR increased in the obstructed kidneys of the DTA and WT animals. Release of obstruction abrogated the obstruction-mediated surge in Tgfb1 levels only in the WT and Ren1d-DTA mice. The Ren1dCre;ROSA-DTA group exhibited elevated levels of Tgfb1 expression even after 2W post-relief of obstruction (I-K) qRT-PCR for αSMA shows a significant decrease at 2W after the release of obstruction in the kidneys of both the WT and Ren1d-DTA mice, but not in the Ren1dCre;ROSA-DTA mice (*P<0.05; †P<0.01; ‡P<0.001; NS non-significant).
