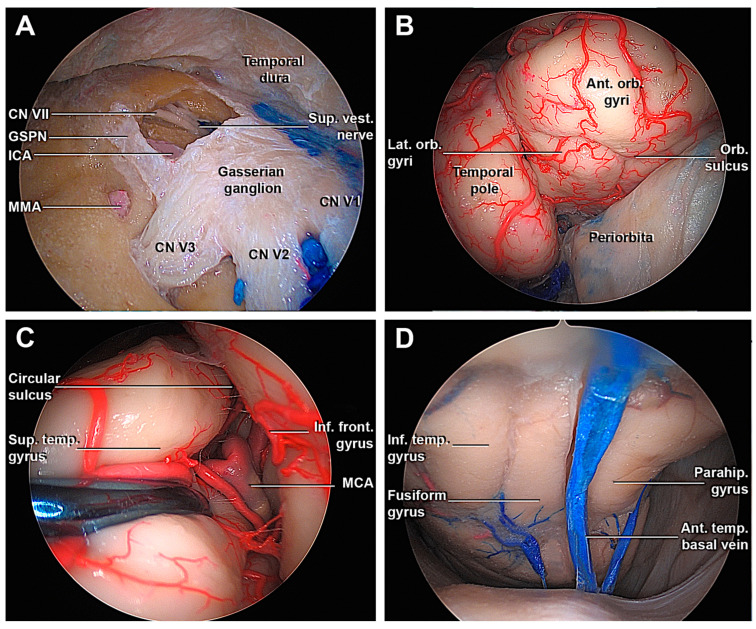
Figure 6.
Transorbital endoscopic approach to the middle fossa. (A) Drilling through the Kawase’s rhomboid, the petrosal tract of ICA, the facial nerve, and the superior vestibular nerve are exposed. (B) The opening of the fronto-temporal dura from an endoscopic transorbital perspective shows the temporal pole and infero-medial portion of the frontal lobe. (C) Following the circular sulcus, it is possible to identify the passages between the M2-M3 segment of the MCA. (D) Detail of the inferior surface of the temporal lobe and its drainage. Ant. Orb. Gyri, anterior orbital gyri; CN, cranial nerve; GSPN, greater superficial petrosal nerve; ICA, internal carotid artery; Inf. Front. Gyrus, inferior frontal gyrus; Inf. temp. Gyrus, inferior temporal gyrus; MMA, middle meningeal artery; Orb. Sulcus, orbital sulcus; Parahip. Gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus; Sup. Temp. gyrus, superior temporal gyrus; Sup. Vest. Nerve, Superior vestibular nerve; V1, ophthalmic division of CN V; V2, maxillary division of CN V; V3, mandibular division of CN V.