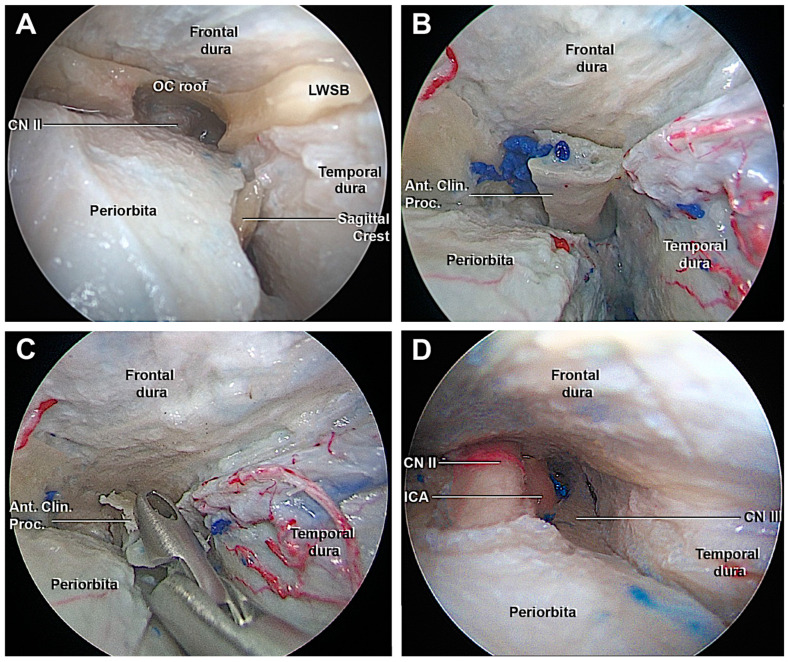
Figure 7.
Endoscopic view of the transorbital extradural anterior clinoidectomy. (A) After the drilling of the orbital surface of the body of the zygomatic bone and the greater sphenoid wing, the optic roof, optic strut, and the lesser sphenoid wing anchor the anterior clinoid process. The roof of the orbital canal is opened to expose the CN II. (B) The interdural dissection of the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus allows to detach the anterior clinoid process from the surrounding dura and facilitate its removal. (C) Removal of the ACP. (D) Final view after the transorbital extradural anterior clinoidectomy. From medial to lateral: the optic nerve, ICA, and third cranial nerve, which are delimited superiorly by the frontal dura, laterally by the temporal dura. Ant. Clin. Proc., anterior clinoid process; CN II, optic nerve, CN III, oculomotor nerve; ICA, internal carotid artery; LWSB, lesser wing sphenoid bone.