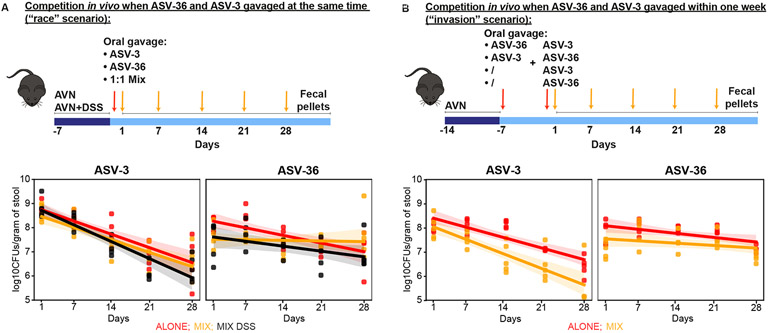
Figure 6. ASV-36-Klebsiella and ASV-3-E. coli competition in the gut of antibiotic and DSS treated animals favors ASV-36.
A) ASV-36-Klebsiella outcompetes ASV-3-E. coli in vivo in a mouse model of antibiotic-induced co-colonization and in the model of epithelial damage through antibiotic treatment in combination with dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) when both strains are inoculated simultaneously (“race scenario”). CFU counts collected over time show a significantly faster decline of ASV-3 in mix with ASV-36 (p<10−3, linear mixed effects model, N=5 per group). B) ASV-36-Klebsiella outcompetes ASV-3-E. coli in vivo in a mouse model of antibiotic-induced co-colonization when strains are orally gavaged in a staggered manner (“invasion scenario”). ASV-3 levels decrease faster in the group of animals pre-colonized with ASV-36 (p=0.065, linear mixed effects model; N=5 animals per group). See also Table S4.