Figure 2. Mechanistic links between shelterin proteins and other hallmarks of aging.
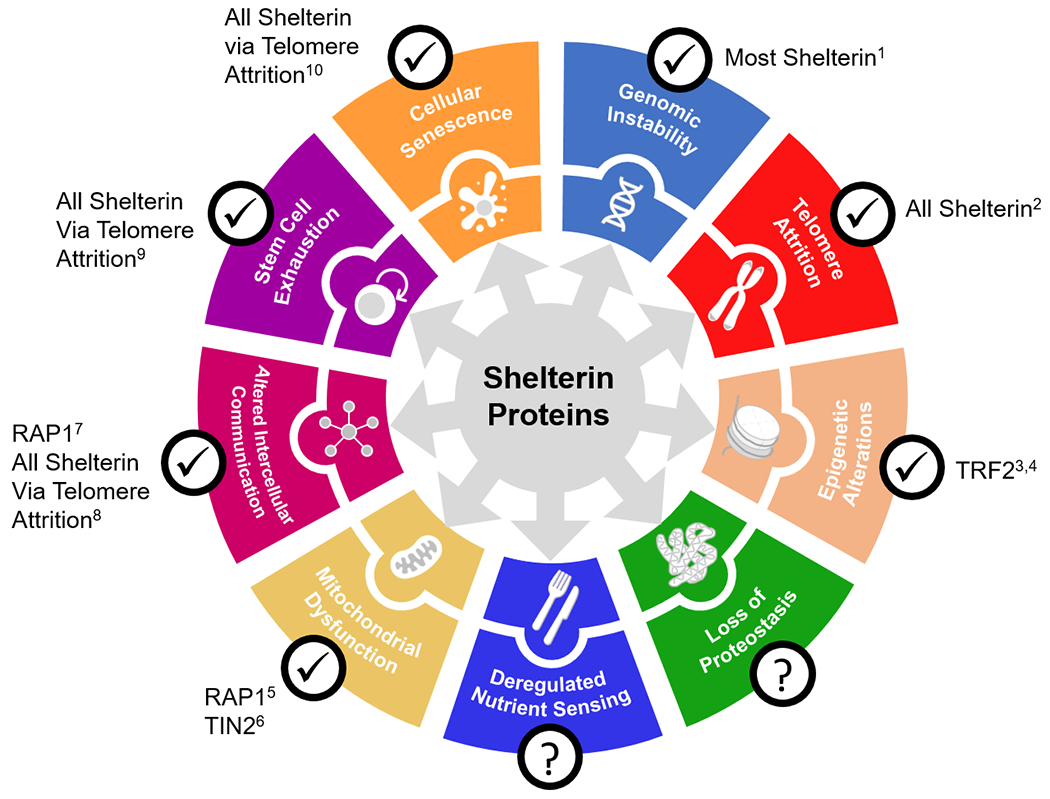
Dysfunctional shelterin protein regulation can induce genomic instability and telomere attrition, thereby contributing indirectly to cellular senescence and its byproducts: altered intercellular communication (e.g., inflammation) and exhaustion of stem cell populations. Shelterin proteins may also directly influence hallmarks of aging such as mitochondrial dysfunction, epigenetic alterations, and intercellular communication, likely alongside other unknown effects. Publications supporting such links are provided, but do not represent an exhaustive list. This figure was adapted from López-Otín et al., 2013, but note that an expanded list of hallmarks is included in López-Otín et al., 2023. References: 1de Lange, 2018; 2Lim et al., 2021; 3Sharma et al., 2021; 4Wang et al., 2007; 5Mukherjee et al., 2018; 6Mukherjee et al., 2019; 7Stock et al., 2022; 8Chen et al., 2012; 9Zhu et al., 2019; 10Martínez & Blasco, 2010.
