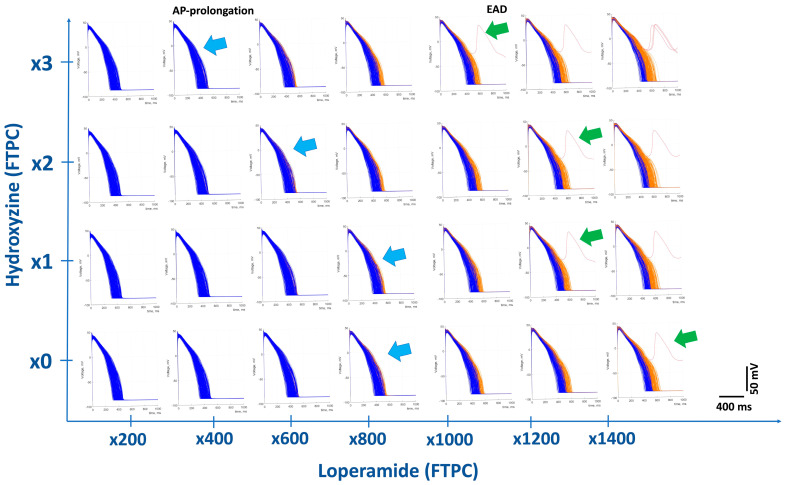
Figure 2.
In silico effects of loperamide alone and in combination with hydroxyzine on simulated populations of action potentials. Modeled evolution of changes in cardiac action potentials (APs) and incidence of early afterdepolarization (EAD) of the cell population at different concentrations of loperamide in relation to its human FTPC using simulation parameters. The bottom row shows traces of the effects of loperamide alone; the upper rows show the effects of loperamide with concurrent hydroxyzine at 1×, 2×, and 3× its FTPC. Combination treatment with hydroxyzine reduced the margin of loperamide to prolong the action potential duration (AP) (from 800× to 400× FTPC) and to elicit early afterdepolarization (EAD) (from 1400× to 1000× FTPC), as noted by the left shifting arrows. Indeed, loperamide in combination with hydroxyzine synergistically prolonged APD90 (at higher multiples) and therefore reduced the safety margin of the risk for QT-prolongation.