Figure 3: dNG and iNG differentially contribute to neocortical PN projection types.
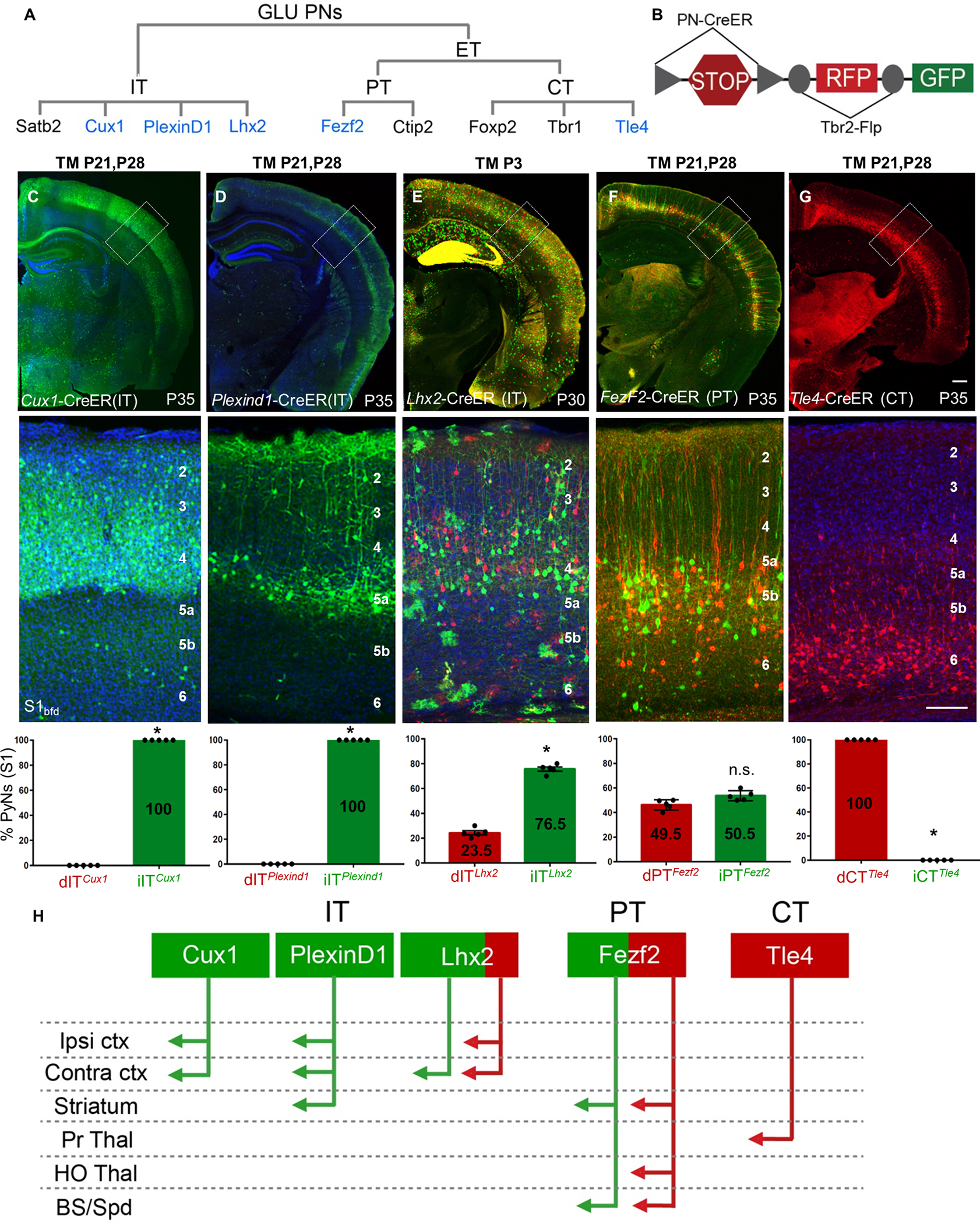
(A) GLU PyNs are subdivided into broad IT and ET classes, and ET consists of PT and CT subclasses. Each of these major classes comprises multiple subpopulations defined by marker gene expression. Genes used for generating CreER driver lines are in blue.
(B) Different PN-CreER driver lines, when combined with IS reporter line Tbr2-Flp, can simultaneously resolve dNG (Cre-NOT-Flp) and iNG (Cre-AND-Flp) derived subpopulations within a marker gene defined PN type.
(C) PNsCux1 (L2–4 ITs, cortico-cortical PNs) and (D) PNsPlexinD1 (subset of L2–5a ITs, cortico-cortical, corticostriatal PNs) were entirely iNG-derived, when corresponding driver lines were induced at P21.
(E) PNsLhx2 (L2–4 ITs) were predominantly generated from iNG (76.5%) when the corresponding driver line was induced at P3.
(F) PNsFezf2 (PTs) were generated equally from dNG and iNG when the driver line was induced at P21.
(G) PNsTle4, a CT subpopulation, were born entirely from dNG.
(C-G) Quantifications performed for differential distribution across dNG and iNG (bottom row). Percentage of dPNs and iPNs indicated on the bar graphs.
(H) dNG (red) and iNG (green) generate distinct genetic and projection defined PN subpopulations across IT, PT, and CT classes. Quantifications (C-G, bottom row) were performed in S1bfd from 5 mice for 750–1500 cells each. Data are mean ± SEM. *P<0.001 (all) except, P(n.s.) = 0.0204 (PNsFezf2), unpaired Student’s t-test. Scale bars, 1mm (low mag); 100μm (high mag). Abbreviations: GLU, glutamatergic pyramidal neurons; IT, intratencephalic, ET, extratelencephalic, PT, pyramidal tract; CT, corticothalamic; S1bfd, primary somatosensory barrel field cortex; Ipsi, ipsilateral; Contra, contralateral; ctx, cortex; Pr Thal, primary thalamus; HO Thal, higher order thalamus; BS, brainstem; Spd, spinal cord; TM, tamoxifen induction. See also Figures S2, S4–S6.
