Figure 4: Proteomics of EV-Enriched Pooled Fractions to Quantify EV Protein Cargoes in Normal and Diseased Vascular and Valvular Tissue.
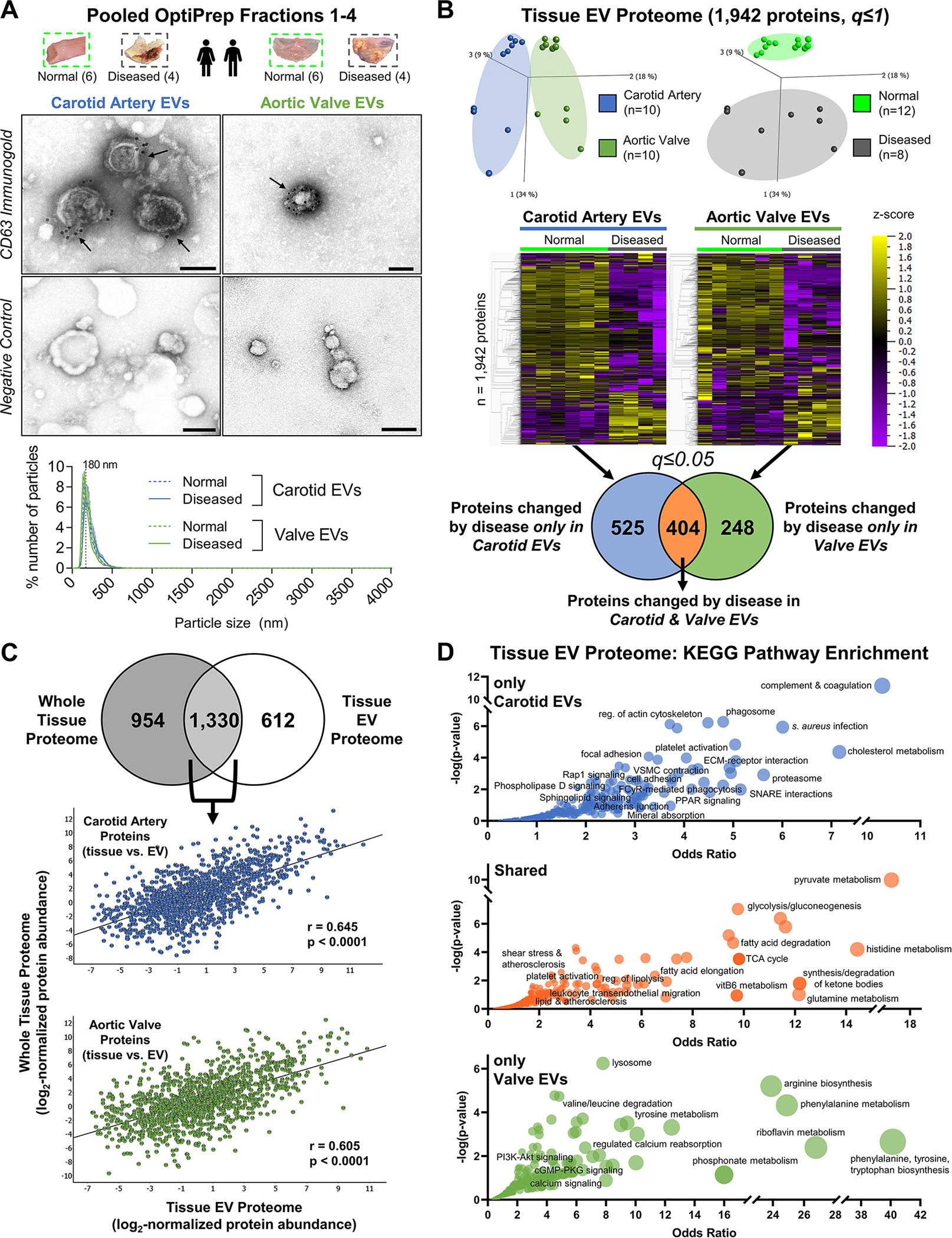
A, Tissue EVs were isolated by density gradient separation from intact normal carotid arteries (n=6 donors), intact diseased carotid artery atherosclerotic plaques (n=4), intact normal aortic valves (n=6), and intact diseased calcified aortic valves (n=4). Representative CD63-labelled immunogold transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and negative control images from pooled fractions 1–4 of intact human carotid artery (left) and aortic valve (right) demonstrated EV enrichment and purification; bar=100 nm. Nanoparticle tracking analysis (bottom, all donors, mean±SEM) found that EVs from intact normal and diseased carotid arteries and aortic valves all had similar mean diameters with a single peak around 200nm, and were isolated without co-enrichment of larger microparticles or apoptotic bodies. B, Isolated tissue EVs from every donor underwent both proteomics and small RNA-seq. The tissue EV proteome was composed of 1,942 proteins. Unfiltered principal component analyses (q≤1) identified tissue- (left) and disease state-specific (right) clustering. Unfiltered heat map analyses (q≤1; ordered by hierarchical clustering) illustrated alterations in individual tissue EV protein abundances between normal and diseased carotid arteries and aortic valves. Abundances of 525 tissue EV proteins were significantly differentially-enriched only between normal and diseased carotid arteries, 248 tissue EV proteins differed only between normal and diseased aortic valves, and 404 tissue EV proteins were significantly altered by disease pathogenesis in both tissue types (significantly-enriched proteins filtered at q≤0.05). C, 68.5% of the tissue EV proteome (1,330 proteins) was also found in the whole-tissue proteome; linear regression identified moderate and statistically significant correlations of per-protein abundances between the whole-tissue and diseased tissue EV proteomes in both carotid artery (Pearson’s r = 0.645, p<0.0001) and aortic valve (Pearson’s r = 0.605, p<0.0001). D, Bubble plots of KEGG pathways that were significantly-enriched amongst tissue EV proteins changed by disease only in carotid arteries (top, 525 proteins), in both carotid arteries and aortic valves (middle, 404 proteins), or only in aortic valves (bottom, 248 proteins) identified shared- and tissue-specific roles of disease-altered cardiovascular tissue EV cargoes. Bubble size corresponds to the percentage of differentially-enriched proteins amongst all pathway constituents.
