Fig. 2: Biochemical classification of 74 patient FH variants provides strong evidence of pathogenicity for many VUS/CI.
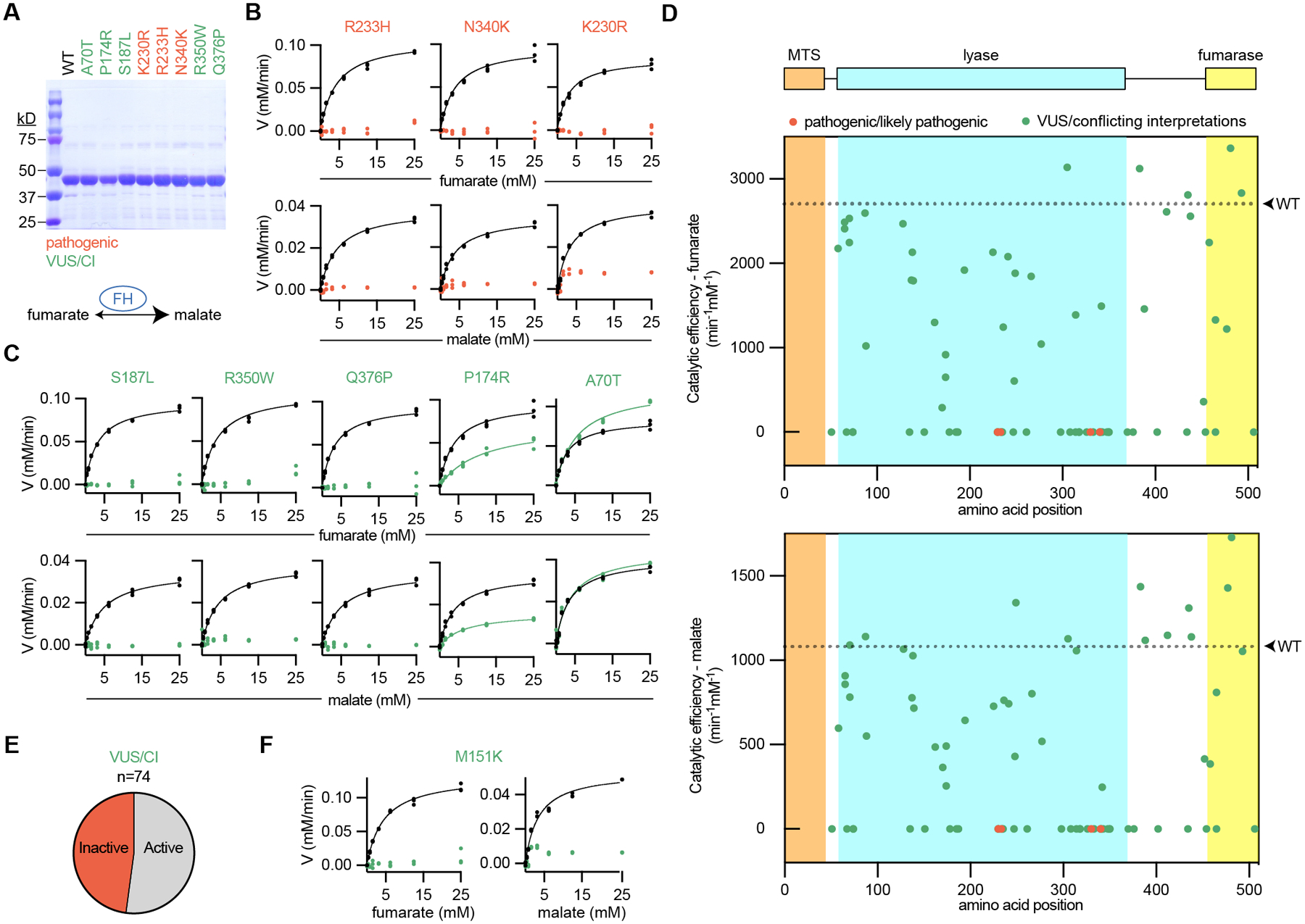
(A) Recombinant FH was produced and purified from E. coli as shown by SDS-PAGE gels stained by Coomassie. Each variant is colored according to the associated interpretation of pathogenicity: pathogenic (red) and VUS/CI (green). For (B-D), recombinant FH was incubated with increasing concentrations of substrate, fumarate (top) or malate (bottom), and the reaction progress was quantified. Wildtype (WT) FH was run simultaneously for each variant, as indicated by the black symbols/lines. (B) All pathogenic variants could not be modeled by Michaelis-Menten kinetics, indicating that these variants are inactive. Michaelis-Menten plots from wildtype enzyme are indicated by black symbols/lines. (C) VUS/CI have a range of enzymatic activities. (D) FH with annotated domains and graphs indicating the catalytic efficiencies of 74 FH variants for fumarate (top) and malate (bottom). For each graph, WT catalytic efficiency is indicated as a dotted line. No variants in the mitochondrial targeting sequence (MTS) were tested because the recombinant FH lacked the first 44 amino acids to improve solubility and purification. (E) Pie chart showing the proportion of VUS/CI that were inactive or active (including partial activity). (F) Graphs showing that M151K (product of FH p.Met151Lys described in Fig. 1) is enzymatically inactive.
