Fig. 10.
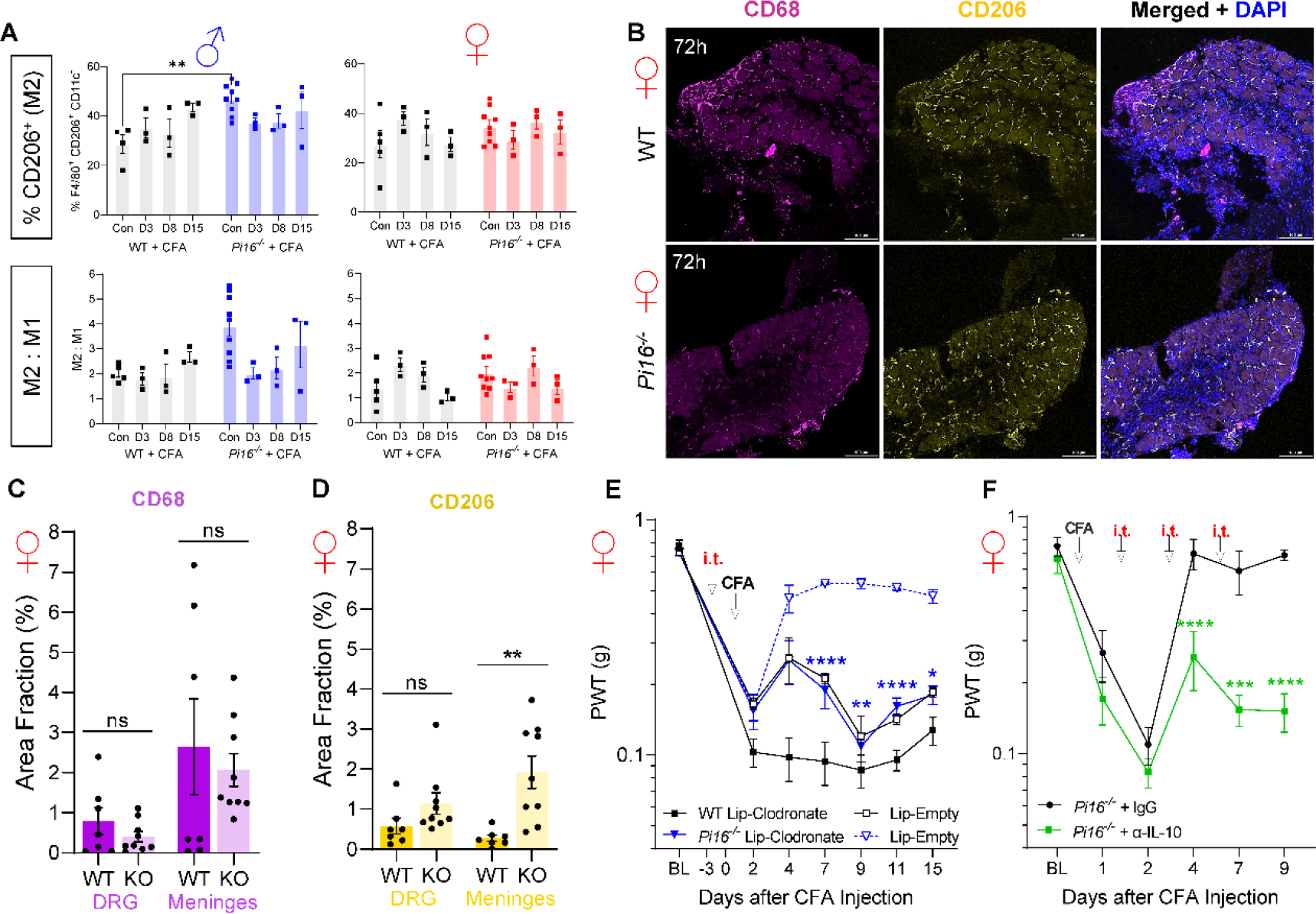
Role of CD206+ cells in resolution of CFA hypersensitivity in Pi16−/− mice. (A) Elevated F4/80+ CD206+ CD11c− cells at baseline in male Pi16−/− DRG (left panels), with no significant differences observed in female DRG (right panels). (B) Representative IHC of CD206hi labeling in female WT and Pi16−/− DRG, quantified in (C-D). A tendency toward decreased CD68 and increased CD206 density were observed in DRG parenchyma from Pi16−/− mice, with a statistically significant increase in meningeal CD206hi cell density in Pi16−/−. (E) Mrc1+ (CD206+) Macrophages were depleted by intrathecal injection of mannosylated clodronate liposomes (Lip-Clodronate), 3 days prior to intraplantar injection of CFA. Pi16−/− mice that received Lip-Clodronate show prolonged hypersensitivity compared to Pi16−/− mice that received drug-free liposomes (Lip-Empty). Lip-Clodronate n=9, Lip-Empty n=3. (F) Following induction of inflammatory pain by intraplantar CFA injection in both hind paws, IL-10 was blocked by intrathecal injection of anti-IL-10 antibody or IgG isotype control on days 1, 2 and 4 post-CFA. On days of i.t. injection, von Frey thresholds were assessed prior to injections. Pi16−/− mice that received anti-IL-10 did not exhibit recovery from CFA-induced hypersensitivity (n=6). Two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni analysis: *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.005, ****P<0.0001.
