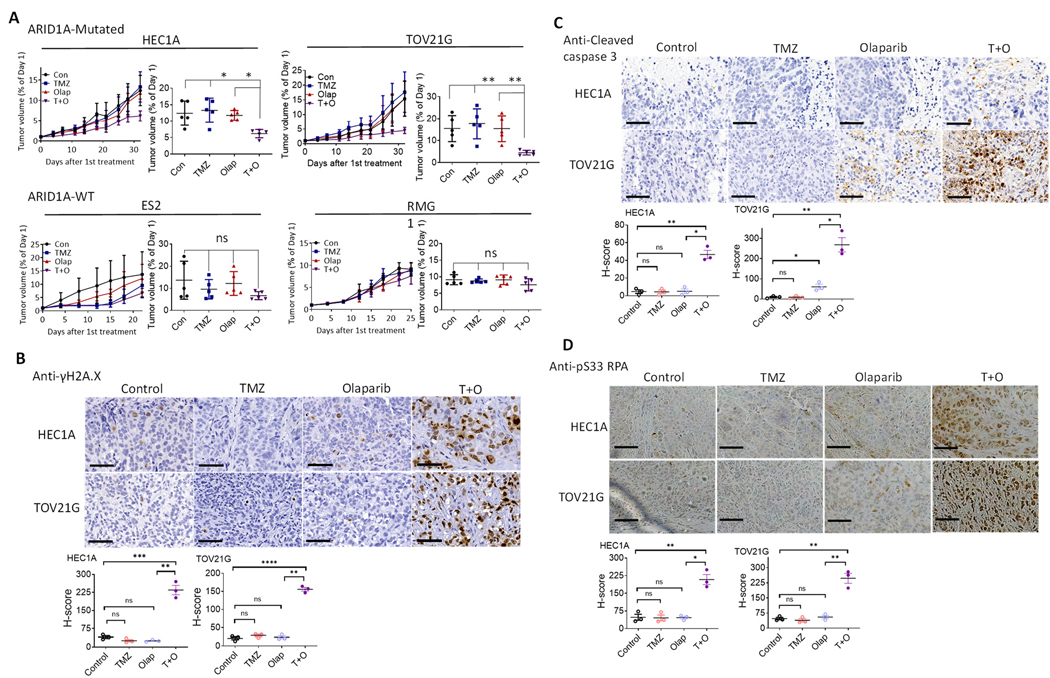
Figure 3. TMZ and Olap combination is effective in treating ovarian xenograft tumors with ARID1A mutations.
(A) In vivo tumor xenografts from ES2, RMG1, HEC1A, and TOV21G cells. Tumor-bearing mice were treated with vehicle (control), TMZ, Olap, or TMZ+Olap (T+O). Tumor growth was measured as tumor volume over a period of 30 days (left) and end point tumor volume compared to day 1 (right). Data are normalized to tumor volume collected at day 1 and presented as mean ± SEM (n = 5). Mann–Whitney test (two-tailed) was used to calculate significance of differences between two comparison groups; *P < 0.01; **P < 0.001.
(B-D) In the two ARID1A-mutant xenograft tumors, HEC1A and TOV21G, the effect of in vivo treatment on replication stress and apoptotic tendency was evaluated using three different markers: γH2A.X (B), cleaved caspase 3 (C), and pS33 RPA (D). (Top) IHC imaging results. Cells expressing the selected markers were immunodetected with DAB. (Bottom) H-score was used to quantify IHC signals of the three markers and is presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3); *P < 05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, Student’s t-test. Scale bar in each photomicrograph represents 60 μm.