Figure 6. The BRD4 C-terminus stabilizes CyclinT1 in the BRD4-PTEFb complex.
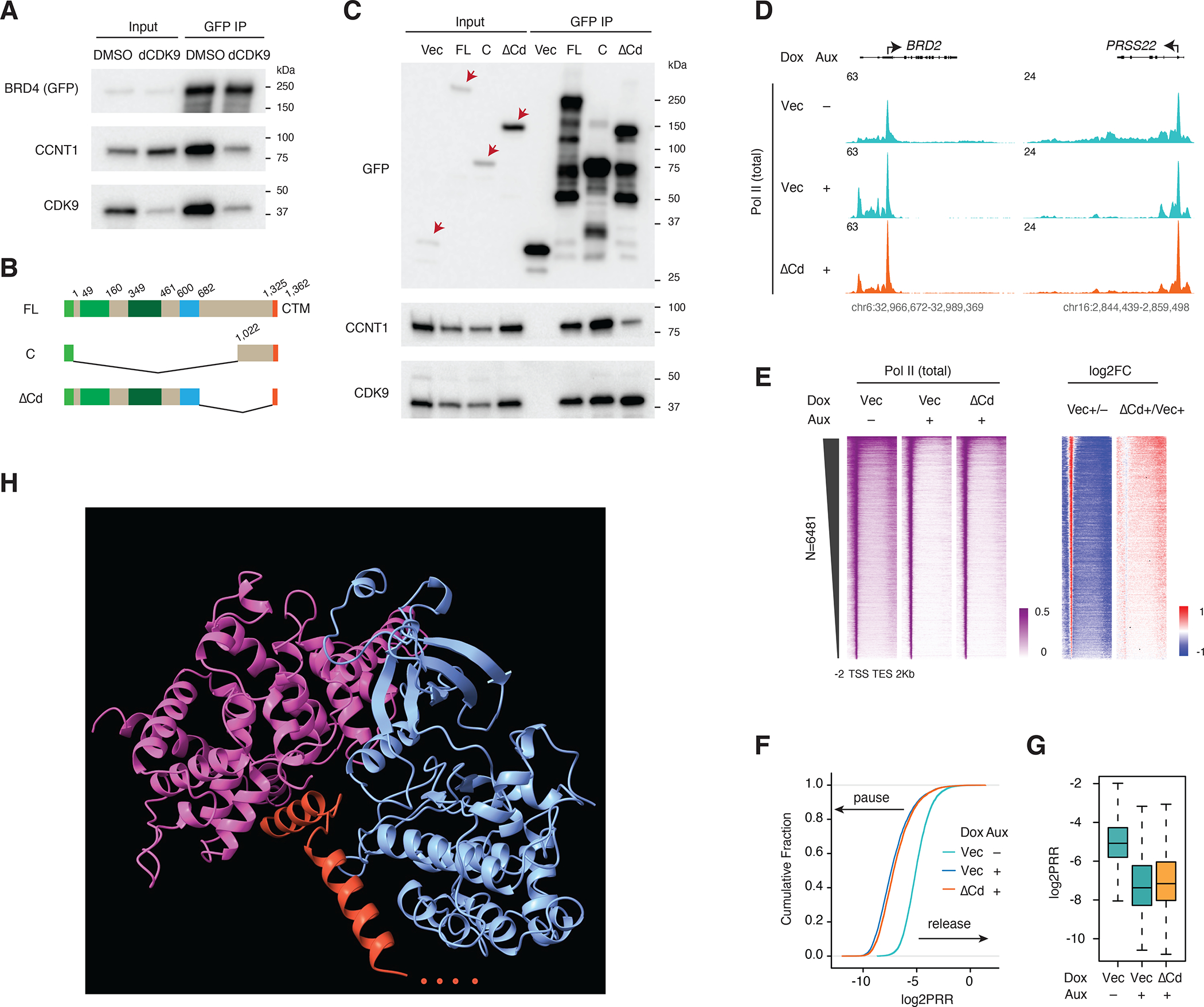
A. Western blot of GFP IP showing the PTEFb complex components associated with BRD4 upon dCDK9 (2.5uM) treatment for 3h. GFP-tagged BRD4 -FL was induced by Dox treatment for 2 days.
B. Schematic of the GFP-tagged constructs: BRD4-FL, BRD4-C and BRD4-ΔCd (deletion of the C-terminal disordered region).
C. Western blot of GFP IP showing PTEFb complex components associated with BRD4 and its C terminal mutants. GFP-tagged BRD4-FL and mutant constructs were induced by Dox treatment for 2 days. Endogenous BRD4 was depleted in all samples by auxin treatment (3h) prior to IP.
D. Track examples for the total Pol II ChIP-seq signal upon BRD4 depletion and rescue by BRD4-ΔCd.
E. Heatmap showing the genome-wide Pol II occupancy and the corresponding fold changes for the rescue experiment in D.
F. ECDF showing the log2PRR for the Pol II ChIP-seq for the rescue experiment in D.
G. Boxplot showing the log2PRR for the Pol II ChIP-seq for the rescue experiment in D.
H. AlphaFold-predicted structure for CTM of BRD4 and the PTEFb complex (344 CDK9 N-terminal residues, 293 N-terminal CCNT1 residues and 37 C-terminal BRD4 residues were used for the computational prediction.
