Figure 1. GINIP binds to the effector binding region of Gαi without affecting its enzymatic activity.
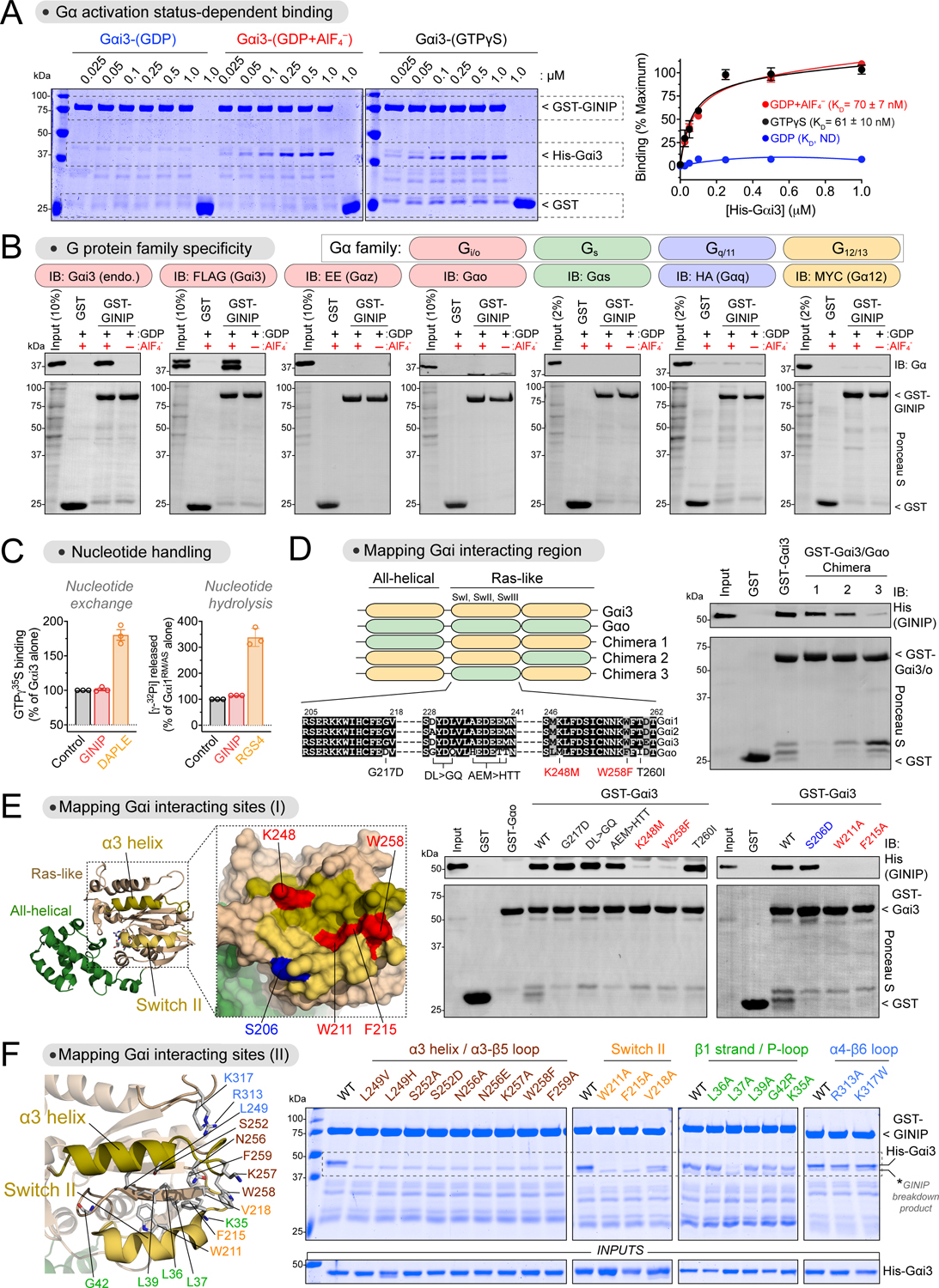
(A) GINIP binds to active but not inactive Gαi3. Left, Coomassie-stained gel showing binding of His-Gαi3, loaded as indicated (GDP, GDP·AlF4−, GTPγS), to immobilized GST-GINIP. Right, quantification of His-Gαi3 binding to GST-GINIP. Mean±S.E.M., n=3–4.
(B) GINIP binds to Gαi3, but not to other Gα’s of the same family (Gαo, Gαz), or other families (Gαs, Gαq, Gα12). Lysates of HEK293T cells expressing the indicated G-proteins were incubated with GST or GST-GINIP immobilized on glutathione-agarose beads in the presence of GDP or GDP·AlF4−. Bead-bound proteins were detected by Ponceau S staining or immunoblotting (IB).
(C) GINIP does not affect the enzymatic activity of Gαi. Nucleotide exchange on Gαi3 was determined by GTPγS binding, whereas nucleotide hydrolysis by Gαi1RM/AS was determined by the production of free phosphate (Pi) from GTP. GINIP, 2 μM, DAPLE, 1 μM, RGS4, 0.2 μM. Mean±S.E.M., n=3.
(D) Gαi3 region aa178–270 is required for GINIP binding. Left, diagram of Gαi3 (orange) /Gαo (green) chimeras. Sequence alignment of Gαi1, Gαi2, Gαi3, and Gαo, indicating mutations tested in panel (E). Right, binding of purified His-GINIP to the indicated G-proteins in the presence of GDP·AlF4−. Bead-bound proteins were detected by Ponceau S staining or immunoblotting (IB).
(E) Mutation of residues in the α3 helix and Switch II of Gαi ablate GINIP binding. Left, Structural model of Gαi1-(GDP·AlF4−) (PDB: 2G83). Red indicates residues in the α3/Switch II region that disrupt GINIP binding when mutated, whereas blue indicates an adjacent residue that does not affect GINIP binding when mutated. Center & Right, binding of purified His-GINIP to the indicated G-proteins in the presence of GDP·AlF4−. Bead-bound proteins were detected by Ponceau S staining or immunoblotting (IB).
(F) Mutation of residues within, but not adjacent to, the effector binding region (α3/Switch II groove) of Gαi impair GINIP binding. Left, Structural model of Gαi1-(GDP·AlF4−) (PDB: 2G83) displaying the residues investigated by site-directed mutagenesis. Right, binding of the indicated G-proteins loaded with GTPγS to GST-GINIP. Bead-bound proteins were detected Coomassie staining.
All protein electrophoresis results are representative of n ≥ 3 experiments. See also Figure S1.
