Figure 2. GINIP directly blocks Gαi-mediated regulation of adenylyl cyclase.
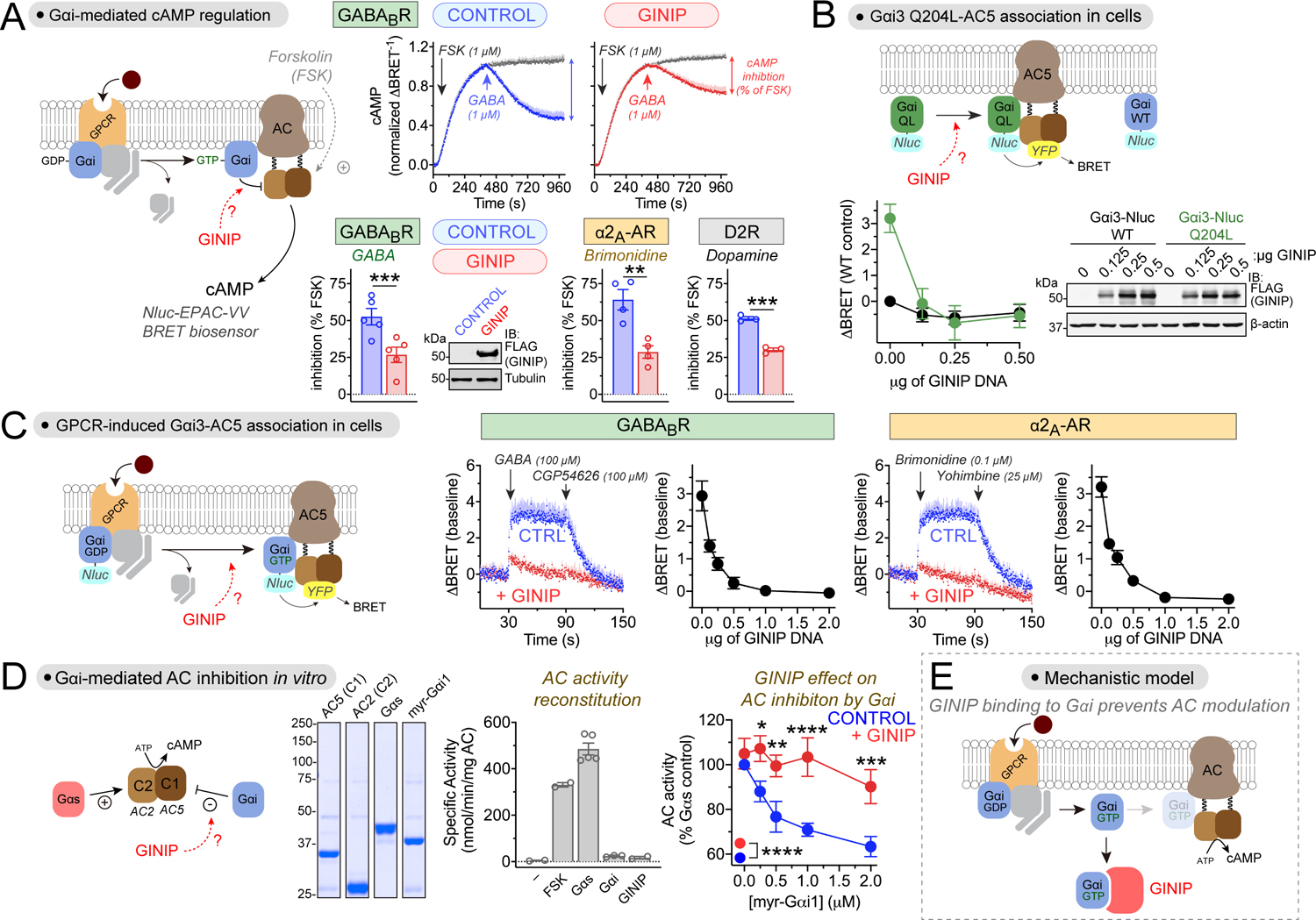
(A) GINIP prevents Gαi-mediated inhibition of adenylyl cyclase (AC) upon stimulation of 3 different GPCRs. Top row, kinetic traces of BRET measurement of cAMP in HEK293T cells expressing the GABABR in the presence or absence of GINIP treated with forskolin (FSK) and GABA as indicated. Bottom row, quantified inhibition of FSK-stimulated cAMP upon stimulation of GABABR, α2A-AR, or D2R with GABA (1 μM), Brimonidine (5 μM), or dopamine (0.2 μM). Immunoblot (IB) validates GINIP expression. Mean±S.E.M., n=3–5. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, paired t-test.
(B) GINIP prevents the association of active Gαi3 with AC5 in cells. Left, changes in BRET (ΔBRET) were determined in HEK293T cells expressing Gαi3-Nluc WT or Gαi3-Nluc Q204L upon transfection of increasing amounts of GINIP. Mean±S.E.M., n=6. Right, validation of GINIP expression by immunoblotting (IB).
(C) GINIP prevents the association of Gαi3 with AC5 upon GPCR stimulation. BRET was measured in HEK293T cells expressing the GABABR or the α2A-AR upon transfection of different amounts of GINIP DNA. Kinetic traces correspond to cells expressing no GINIP (‘CTRL’ blue) or transfected with 2 μg of GINIP plasmid (red). Cells were treated with the indicated GPCR agonists/antagonists. Mean±S.E.M., n=3.
(D) GINIP blocks the regulation of AC by Gαi in vitro. Coomassie-stained gel shows the purified proteins used. Bar graph shows that FSK (5 μM) or Gαs-GTPγS (0.1 μM), but not myr-Gαi1 (2 μM) or GINIP (2 μM), promote the activation of reconstituted AC (AC5 (C1) + AC2 (C2)). Right, Gαs-stimulated AC activity in the presence of increasing concentrations of myr-Gαi1-GTPγS with (red) or withiot (blue) GINIP (2 μM). Mean±S.E.M., n=5. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, two-way ANOVA for presence/ absence of GINIP x myr-Gαi1 concentration, with multiple comparisons at each concentration using Fisher’s LSD test.
(E) Diagram summarizing the proposed mechanism action of GINIP on Gαi-mediated modulation of AC activity (competitive binding).
