Figure 3. GINIP promotes Gβγ-mediated signaling by antagonizing the action of RGS GAPs on Gαi.
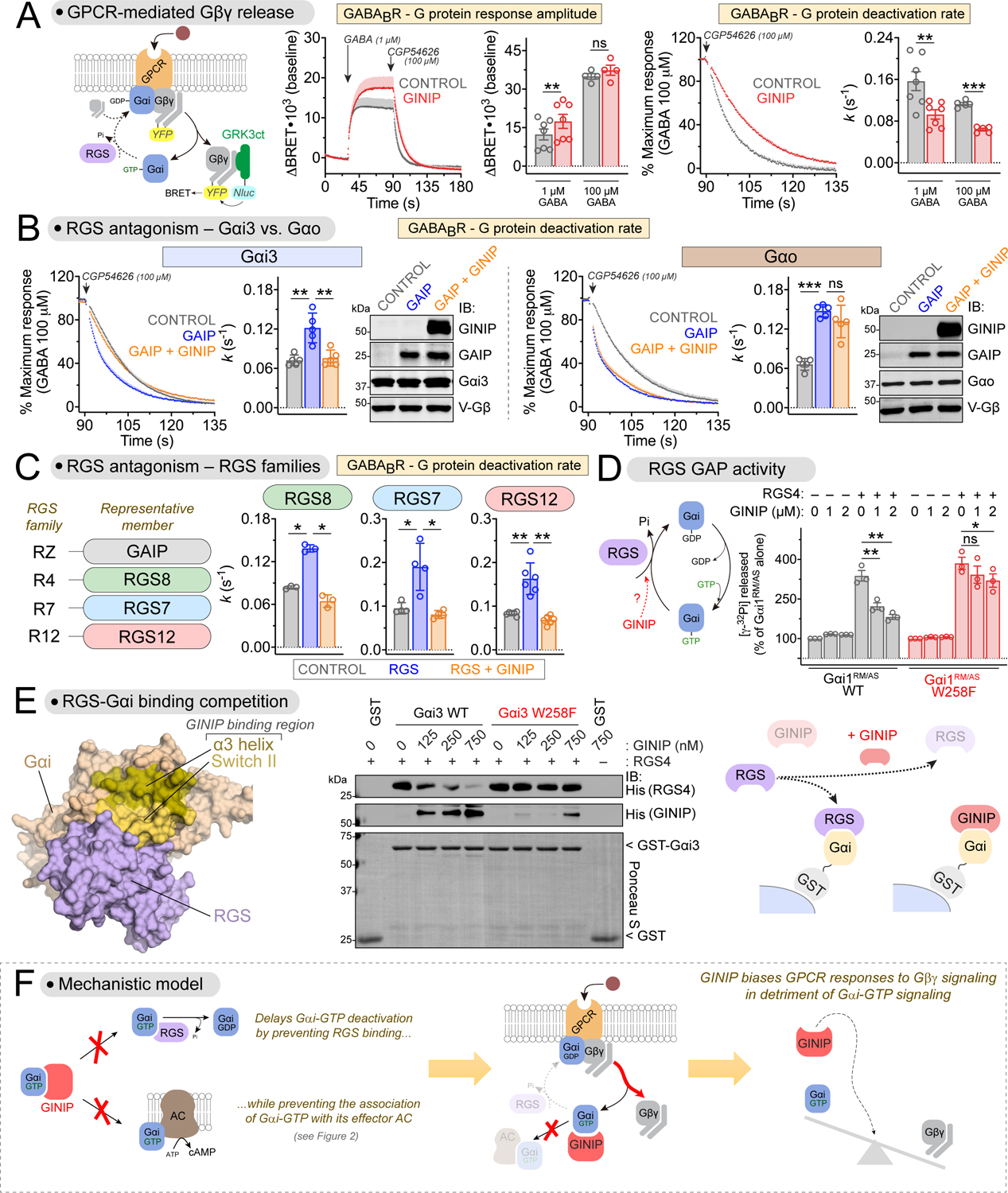
(A) GINIP enhances Gβγ-mediated signaling triggered by GABABR. Left, diagram of G-protein activation/deactivation cycle and BRET-based detection of free Gβγ. Center, BRET was measured in HEK293T cells expressing the GABABR in the absence (black) or presence (red) of GINIP. Cells were treated with GABA and CGP54626 as indicated. Right, G protein deactivation rates were determined by normalizing the BRET data and curve fitting to extract rate constant values (k). Mean±S.E.M., n=4–7. ns = not significant, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, paired t-test.
(B) GINIP antagonizes GAIP-mediated acceleration of Gβγ deactivation for Gi but not Go proteins. BRET experiments were carried out and analyzed as in (A) with cells expressing Gαi3 or Gαo in the absence (grey) or presence of GAIP (blue) or GAIP plus GINIP (orange). GAIP and GINIP expression validated by immunoblotting (IB). Mean±S.E.M., n=5. ns = not significant, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, one-way ANOVA corrected for multiple comparisons (Tukey).
(C) GINIP antagonizes the acceleration of Gβγ deactivation mediated by representative members of all RGS families. BRET experiments were carried out and analyzed as in (B), except that RGS8 (R4), RGS7 (R7), or RGS12 (R12) were used instead of GAIP (RZ). RGS7 was co-transfected with Gβ5 and R7BP. Mean±S.E.M., n=3–6. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, one-way ANOVA corrected for multiple comparisons (Tukey).
(D) GINIP antagonizes the GAP activity of RGS4 on Gαi in vitro. Nucleotide hydrolysis by Gαi1RM/AS (WT or W258F) was determined in the presence of RGS4 and/or GINIP. Mean±S.E.M., n=3. ns = not significant, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, one-way ANOVA corrected for multiple comparisons (Tukey).
(E) GINIP competes with RGS4 for binding to Gαi3. Left, Structural model of Gαi1-(GDP·AlF4−) bound to RGS4 (PDB: 1AGR). Right, increasing concentrations of purified His-GINIP and a fixed amount of His-RGS4 (20 nM) were incubated with GST or GST-Gαi3 (WT or W258F) immobilized on glutathione-agarose beads in the presence of GDP·AlF4−. Bead-bound proteins were detected by Ponceau S staining or by immunoblotting (IB). One representative result of three independent experiments is shown.
(F) Diagram summarizing the proposed mechanism by which GINIP biases G protein responses by favoring Gβγ-dependent signaling in detriment of Gαi-dependent signaling.
