Figure 2. CB1R modulation of intracellular signaling pathways.
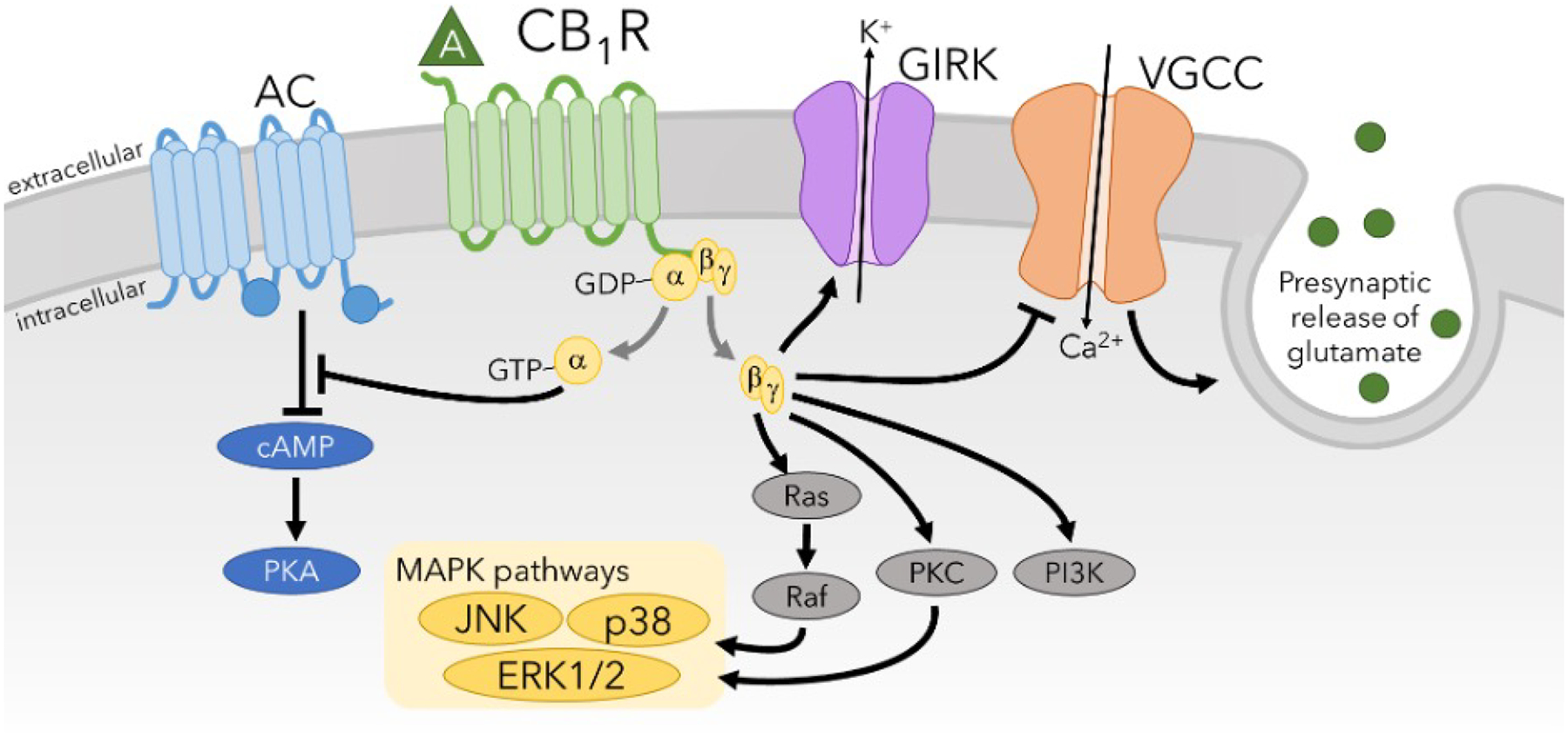
Agonist-induced activation by CB1R causes inhibition of VGCCs and adenylyl cyclase and production of cAMP while stimulating GIRK potassium channels and MAPK signaling pathways such as extracellular-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2, JNK, and p38. Activation of CB1R also increases PKC and PI3K signaling pathways. A major overall effect of CB1R activation is that it inhibits neuronal signaling by preventing neurotransmitter release (inhibition of VGCCs) and hyperpolarization of the membrane potential (activation of GIRKs).
