Figure 4. Proximal aortic valve (AoV) Prox1 targets, including lymphatic EC genes, were identified using CUT&RUN technology.
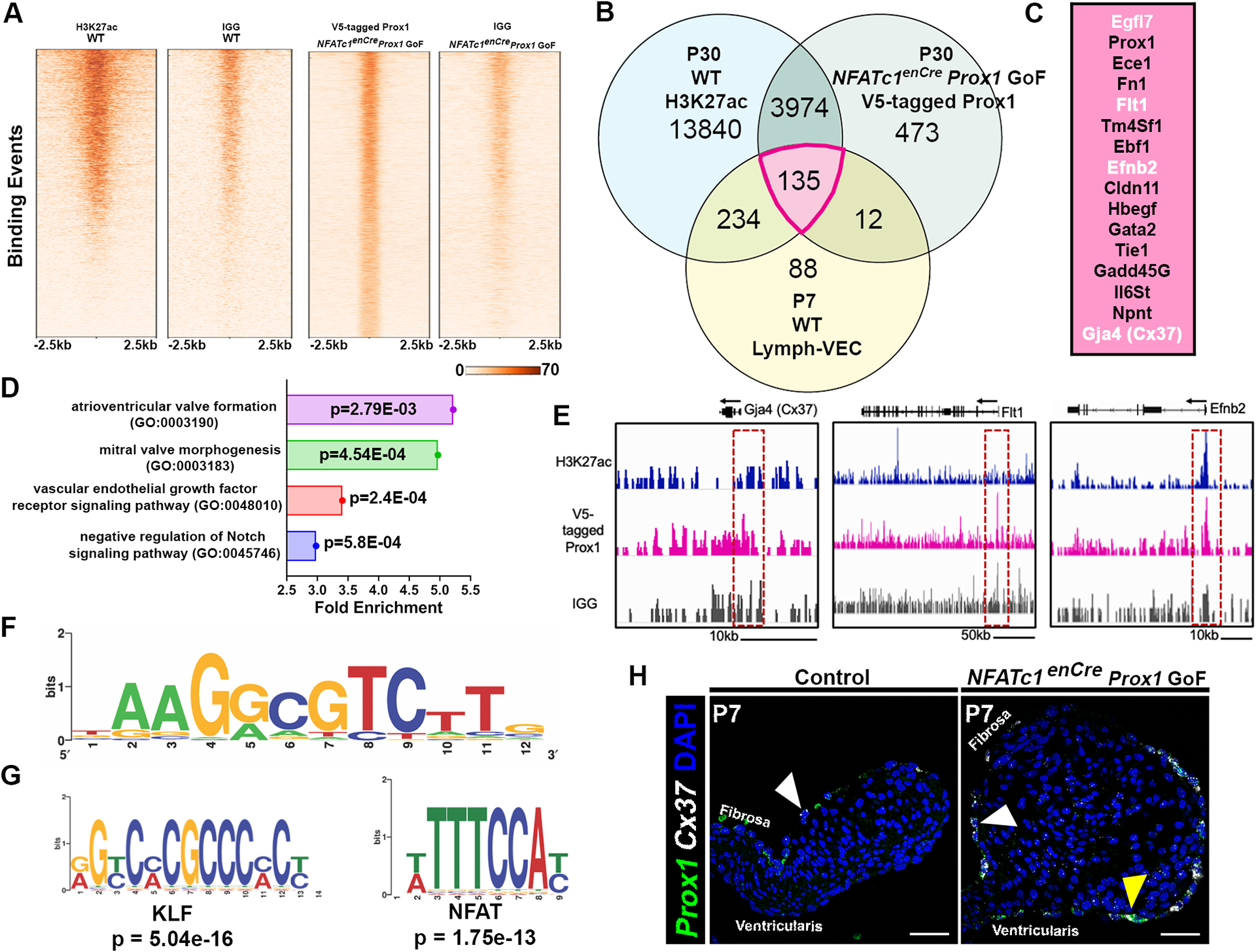
A, Peak distribution of Prox1-binding sites in the mouse genome (mm10) in one control group (mouse IgG) and one experimental (V5 antibody) group as determined by CUT&RUN. B, Venn diagram showing overlap in the number of genes with open chromatin marker H3Kac27 (blue), enriched binding sites for V5-tagged Prox1, and enrichment in the Lymph-VEC VEC population at P7. C, The top P7 Lymph-VEC differentially expressed genes with open chromatin marker H3K27ac and enriched with V5-tagged Prox1 binding sites (B, Pink (135 genes)). Genes in white font were subsequently validated in vivo. D, A biological GO term analysis of genes adjacent to V5-tagged Prox1 binding sequences includes key signaling pathways found in heart valve development including the VEGF signaling pathway. E, The visualized exogenous V5-tagged Prox1 binding peaks associated with a known Prox1 target Gja4 (Cx37), and potential VEC Prox1 targets Flt1 and Efnb2. F, A V5-tagged Prox1 binding motif similar to reported Prox1 binding motifs was identified in candidate target gene sequences. G, A differential motif enrichment analysis was performed to identify potential Prox1 partners based on consensus site localization in proximity to putative Prox1 binding sites. H, Expression of the known Prox1 target gene Cx37 (white) is colocalized with ectopic Prox1+ (green) VECs at P7 in NFATc1enCre Prox1 GoF AoV as determined by RNA in situ hybridization (G’). White arrowheads indicate Prox1+ Cx37+ fibrosa side VEC. Yellow arrowheads indicate ectopic Prox1+ Cx37+ ventricularis side VEC. Scale bar =50μm.
