Abstract
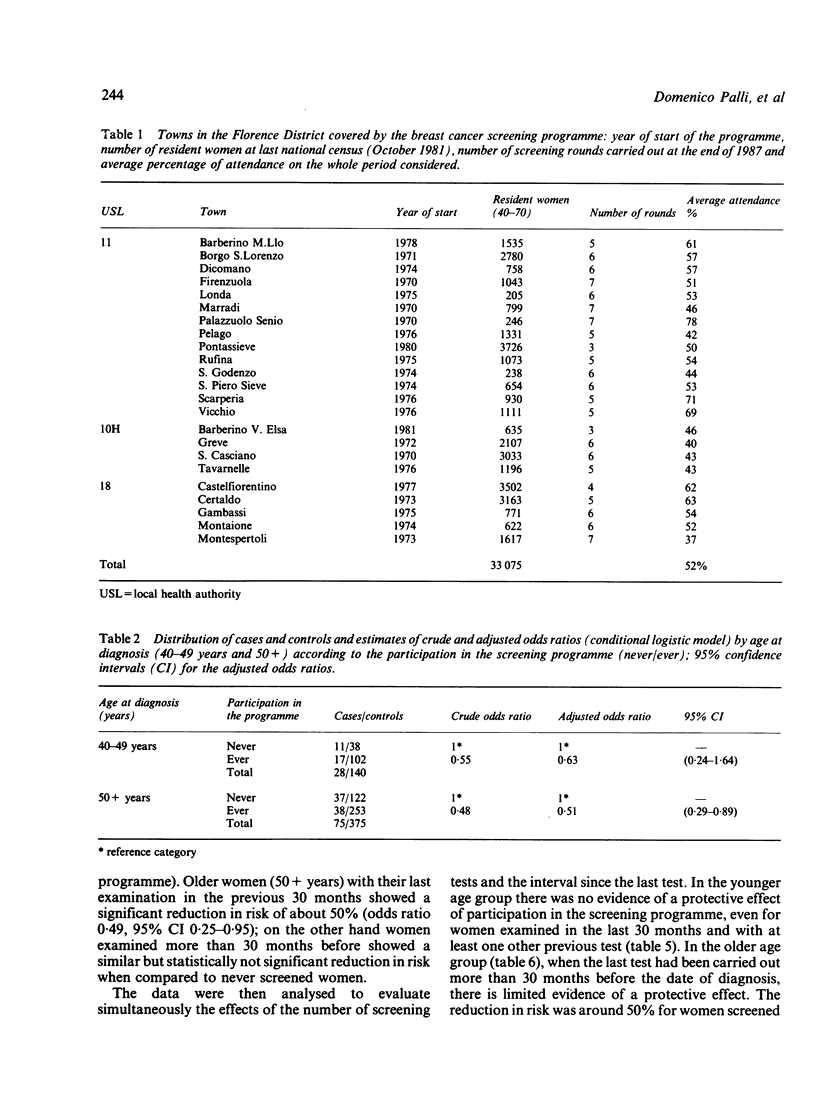
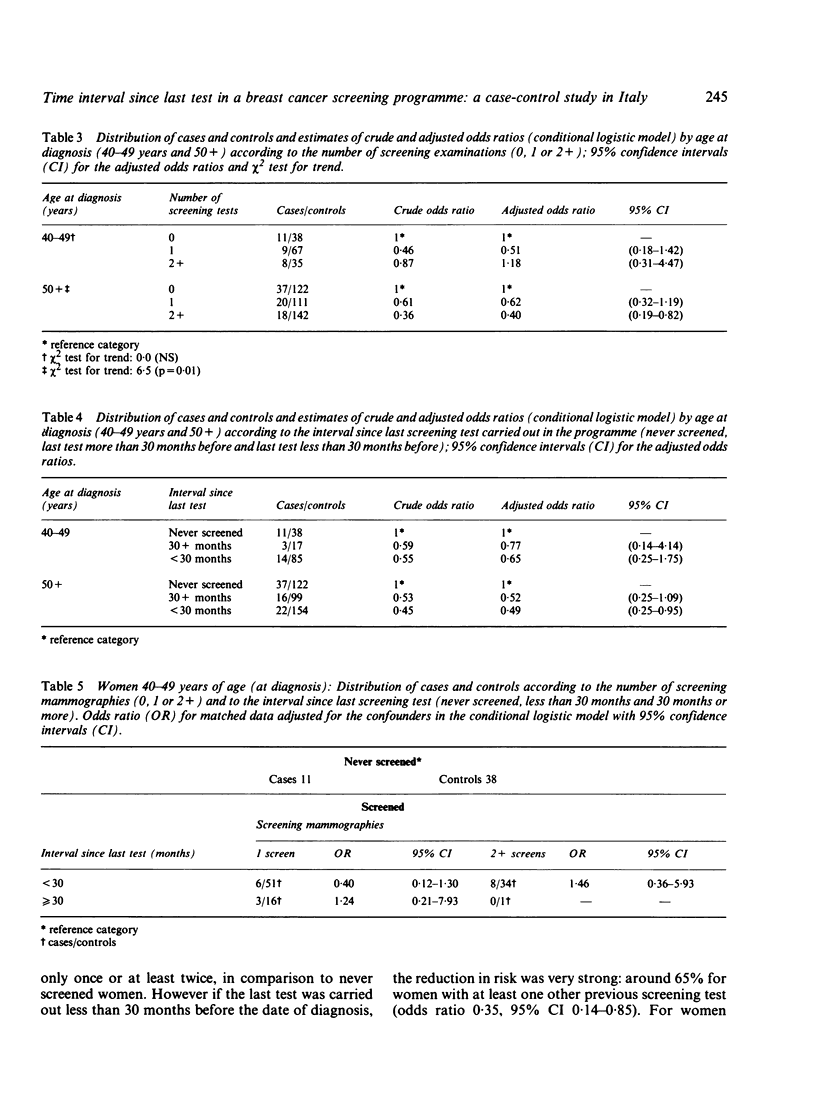
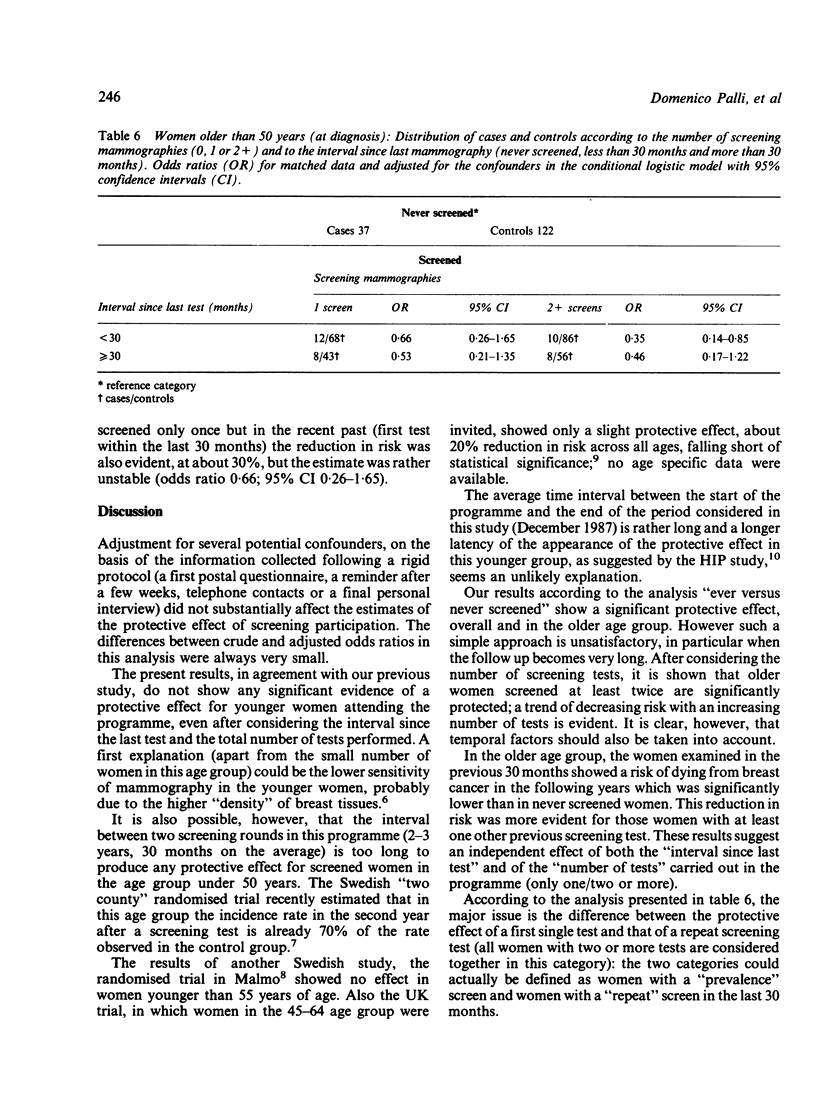
STUDY OBJECTIVE: To evaluate a population based screening programme for breast cancer. DESIGN: This was a case-control study of women dying of breast cancer between 1977 and 1987 who had been invited to take part in a screening programme. SETTING: Community based study of women aged between 40 and 70 years (total population about 35,000 at 1981 census), living in 23 small towns near Florence, Italy. PARTICIPANTS: 103 cases were identified from death certification, and 515 living controls (five per case) selected for year of birth and town of residence. MEASUREMENTS AND MAIN RESULTS: Screening history was obtained from computer archive. Sociodemographic information was obtained from town registry offices and directly from relatives of the deceased and from the controls by postal questionnaire, and if necessary telephone or personal interview. Analysis was carried out on two age groups--40-49 years and 50+ years at diagnosis--and considered the number of screening tests and the time interval since the last test, separately and together. In the older age group, women with at least one screening test in the previous 2 1/2 years showed a 50% reduction in risk (odds ratio 0.49, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.25-0.95). If they had also had another previous negative screen the risk was reduced to one third (odds ratio 0.35, 95% CI 0.14-0.85). There was a significant trend of decreasing risk with increasing number of screens in older women. No clear evidence of a similar protective effect was shown for women in the 40-49 year age group. CONCLUSIONS: A significant protective effect of the screening programme is evident in older women but not in younger ones. The data do not allow an assessment of optimal screening interval because of the small number of previously screened cases.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson I., Aspegren K., Janzon L., Landberg T., Lindholm K., Linell F., Ljungberg O., Ranstam J., Sigfússon B. Mammographic screening and mortality from breast cancer: the Malmö mammographic screening trial. BMJ. 1988 Oct 15;297(6654):943–948. doi: 10.1136/bmj.297.6654.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collette H. J., Day N. E., Rombach J. J., de Waard F. Evaluation of screening for breast cancer in a non-randomised study (the DOM project) by means of a case-control study. Lancet. 1984 Jun 2;1(8388):1224–1226. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91704-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habbema J. D., van Oortmarssen G. J., van Putten D. J., Lubbe J. T., van der Maas P. J. Age-specific reduction in breast cancer mortality by screening: an analysis of the results of the Health Insurance Plan of Greater New York study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Aug;77(2):317–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palli D., Del Turco M. R., Buiatti E., Carli S., Ciatto S., Toscani L., Maltoni G. A case-control study of the efficacy of a non-randomized breast cancer screening program in Florence (Italy). Int J Cancer. 1986 Oct 15;38(4):501–504. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910380408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosselli Del Turco M., Giannardi G., Villari N. The diagnostic efficacy of mammography and palpation in early detection of breast cancer. Tumori. 1980 Feb;66(1):85–92. doi: 10.1177/030089168006600109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S., Strax P., Venet L. Periodic breast cancer screening in reducing mortality from breast cancer. JAMA. 1971 Mar 15;215(11):1777–1785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabár L., Faberberg G., Day N. E., Holmberg L. What is the optimum interval between mammographic screening examinations? An analysis based on the latest results of the Swedish two-county breast cancer screening trial. Br J Cancer. 1987 May;55(5):547–551. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbeek A. L., Hendriks J. H., Holland R., Mravunac M., Sturmans F., Day N. E. Reduction of breast cancer mortality through mass screening with modern mammography. First results of the Nijmegen project, 1975-1981. Lancet. 1984 Jun 2;1(8388):1222–1224. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91703-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


