Fig. 1. Impact of transient exposure to the CSF1R antagonist PLX5622 (2-weeks “ON” and 7-weeks “OFF”) on open-field behaviors in preformed fibril-injected aged mice.
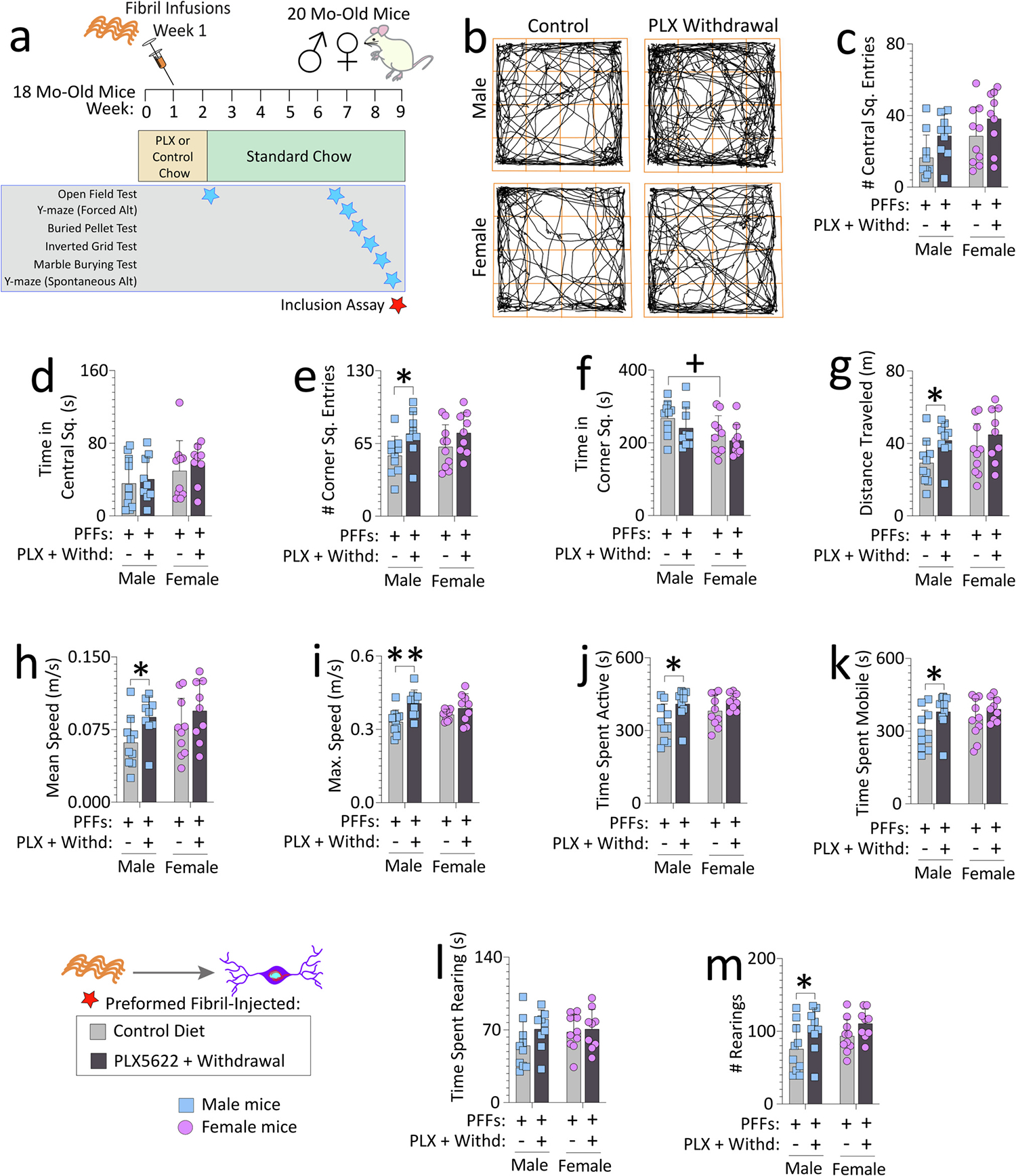
Aged, outbred CD-1 mice of both sexes were fed special chow with or without the CSF1R inhibitor, PLX5622, for two weeks, and then fed standard rodent chow for an additional 7 weeks. Preformed fibrils (PFFs; 5 μg in 1 μL) were injected into the bulbar anterior olfactory nucleus seven days after initiation of the PLX5622 diet (a). For evidence of PLX5622-driven depletion and repopulation of microglia/macrophages, see Figs. S4 and S10a. Mice were tested in an open-field arena after PLX5622 withdrawal (timeline in a; data for the open-field test during PLX5622 delivery are in Fig. S6). (b) Representative trackplots from ANY-maze. Numbers of central square entries (c) and the time spent in central squares (d) are shown. Numbers of corner square entries (e), time spent in corner squares (f), distance traveled (g), mean speeds (h), maximum speeds (i), time spent active (such as grooming) (j), time spent mobile (moving) (k), time spent rearing (l), and numbers of rears (m) are shown. Out of n = 40 PFF-infused mice, two mice were sacrificed early due to dermatitis and an abdominal abscess and thus excluded from the open field test (see Methods). Each mouse is illustrated as a colored dot on bar graphs with group means + SDs. *p ≤ 0.0500, **p ≤ 0.0100 for control diet vs. transient dietary PLX5622; +p ≤ 0.0500 for male vs. female two-way ANOVA/Bonferroni. All testing was two-tailed.
