FIGURE 6. A case of mycobacteriophage-resistant M. abscessus infection.
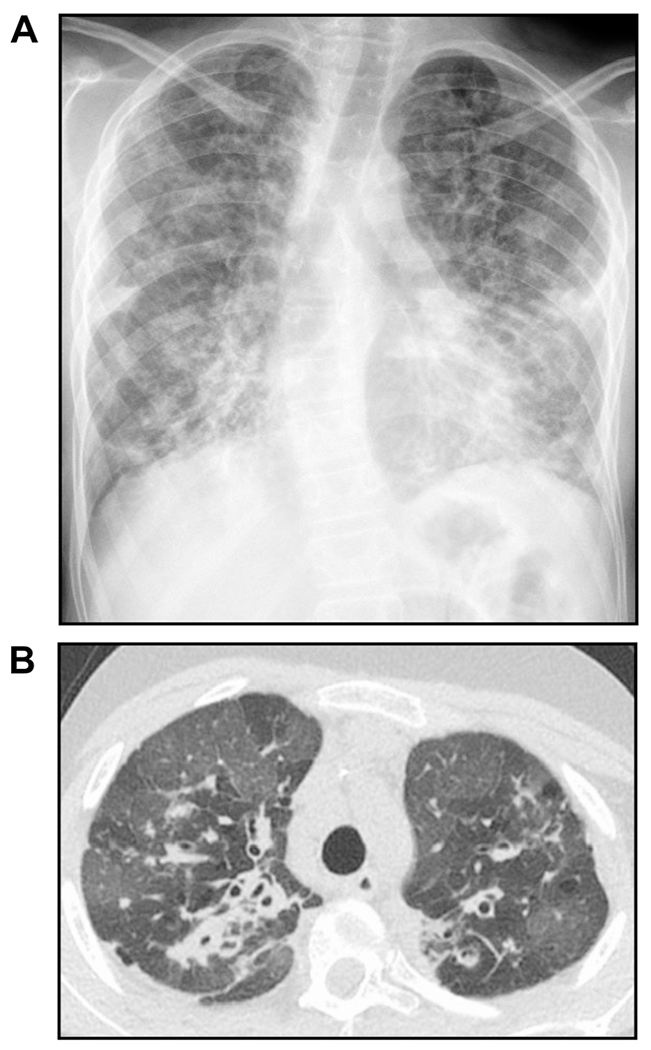
(A) Plain chest radiograph and (B) computed tomography of the chest showing advanced bronchiectasis in an adolescent with cystic fibrosis and CFTR genetic mutations not amenable to CFTR modulator. The patient presents for lung transplant evaluation, but that was delayed due to sputum being both AFB stain positive and culture positive for M. abscessus. Standard and investigational therapies were unsuccessful in clearing the positive AFB sputum stain to allow consideration for transplant at that time, so intravenous Mycobacteriophage therapy was instituted that eventually cleared the positive AFB sputum stain. However, after one-year of phage therapy, the patient developed neutralizing antibodies against the phage leading to the return of the AFB sputum stain positivity. Images courtesy of Don Hayes Jr.
