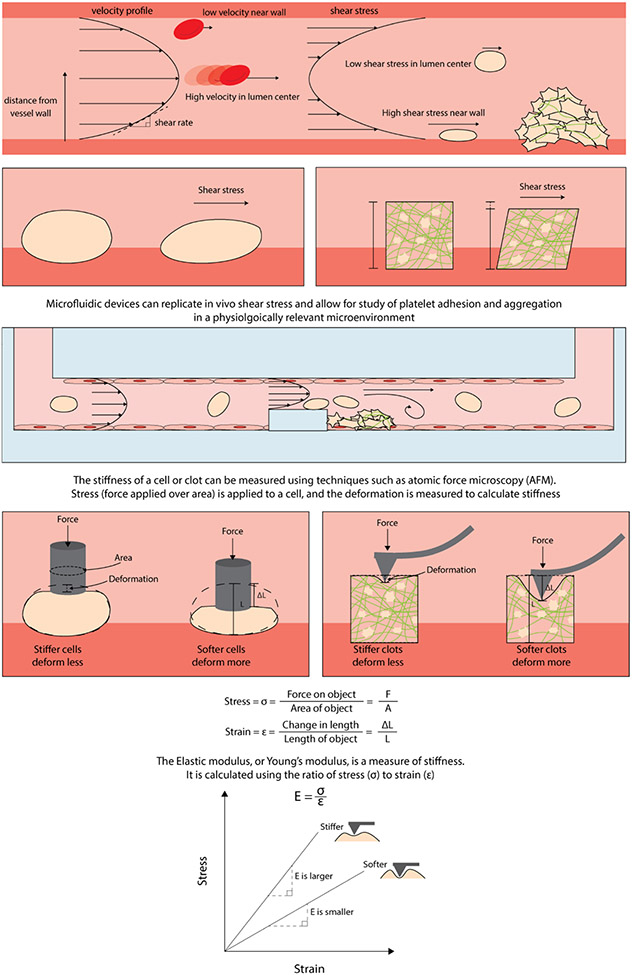
FIGURE 1.
Biophysics of shear flow and cell stiffness. Fluid flowing through a blood vessel reaches a steady state with a parabolic velocity profile. Shear rate is the change in velocity as the fluid distance from the vessel wall increases. Shear stress is a measure of how much force is acting on an object and is proportional to shear rate and fluid viscosity. Platelets aggregate with fibrin to form a network to develop a clot. The ability to control geometric constraints and endothelialize microfluidics has enabled in vitro studies that closely mimic the in vivo microenvironment. Clot stiffness changes over the course of contraction and deforms as platelets mechanically remodel the fibrin network.