Figure 2. α2δ−1 inhibition with gabapentin diminishes FK506-induced increases in presynaptic and postsynaptic NMDAR activity in spinally projecting PVN neurons.
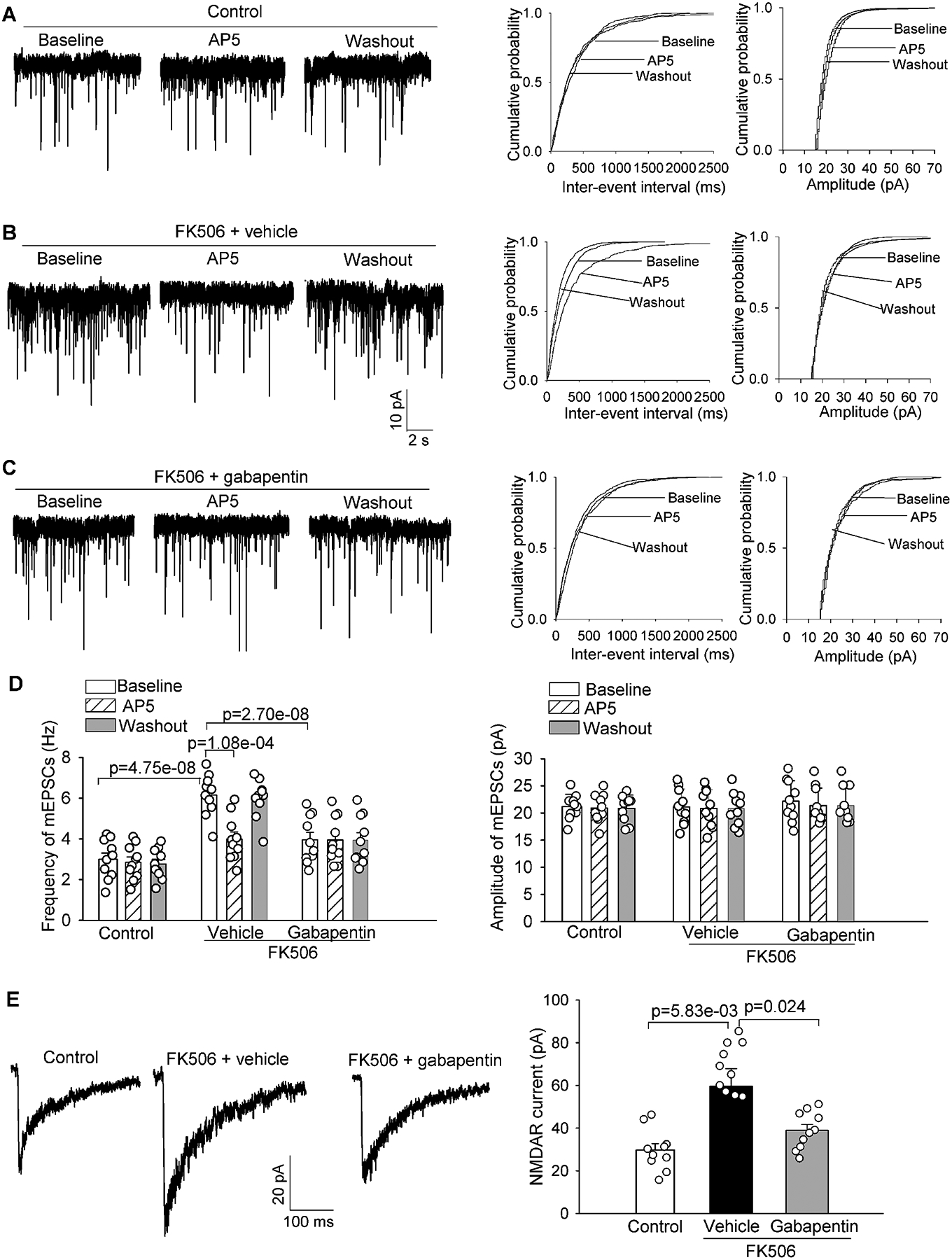
A-C, Representative recording traces and cumulative probability plots show the effects of bath application of 50 μM AP5 on the frequency and amplitude of miniature of excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSCs) of spinally projecting PVN neurons in brain slices pretreated with 100 μM gabapentin in FK506-treated rats. D, Summary data show the effects of gabapentin and AP5 on the frequency and amplitude of mEPSCs of labeled PVN neurons in vehicle-treated control rats and FK506-treated rats (n = 10 neurons from 4 male rats per group). E, Representative recording traces and quantification show the effect of gabapentin (100 μM) on the amplitude of puff-elicited NMDAR currents in labeled PVN neurons in brain slices from FK506-treated rats (n = 10 neurons from 4 male rats per group). The repeated measures models were fitted for statistical analysis.
