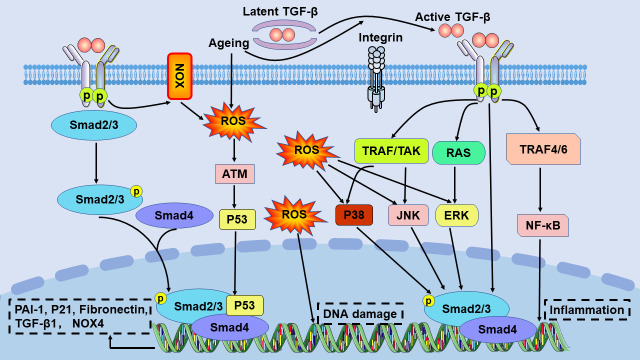
Figure 3.
The TGF-β signalling pathway in aging and fibrosis. TGF-β is an inactive complex formed by the combination of TGF-β with a latency-associated peptide. Latent activation of TGF-β in fibrotic illnesses may involve ROS, aging, and integrins. NOX is one of the key enzymes linking ROS and TGF-β activity. Different NOX subtypes contribute to the production of intracellular ROS. ROS overproduction can lead to DNA damage. ROS interacts with classical and nonclassical TGF-β signalling pathways to regulate inflammation and the expression of the PAI-1, P21, fibronectin, TGF-β, and NOX4 genes. ATM, ataxia telangiectasia mutated protein; JNK, c-Jun terminal kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; NOX, NADPH oxidase; PAI-1, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TAK1, TGF-β-activated kinase 1; TRAF, TGF-β receptor-associated factor.