Figure 1: HLA-DP risk haplotype for UC binds to NKp44.
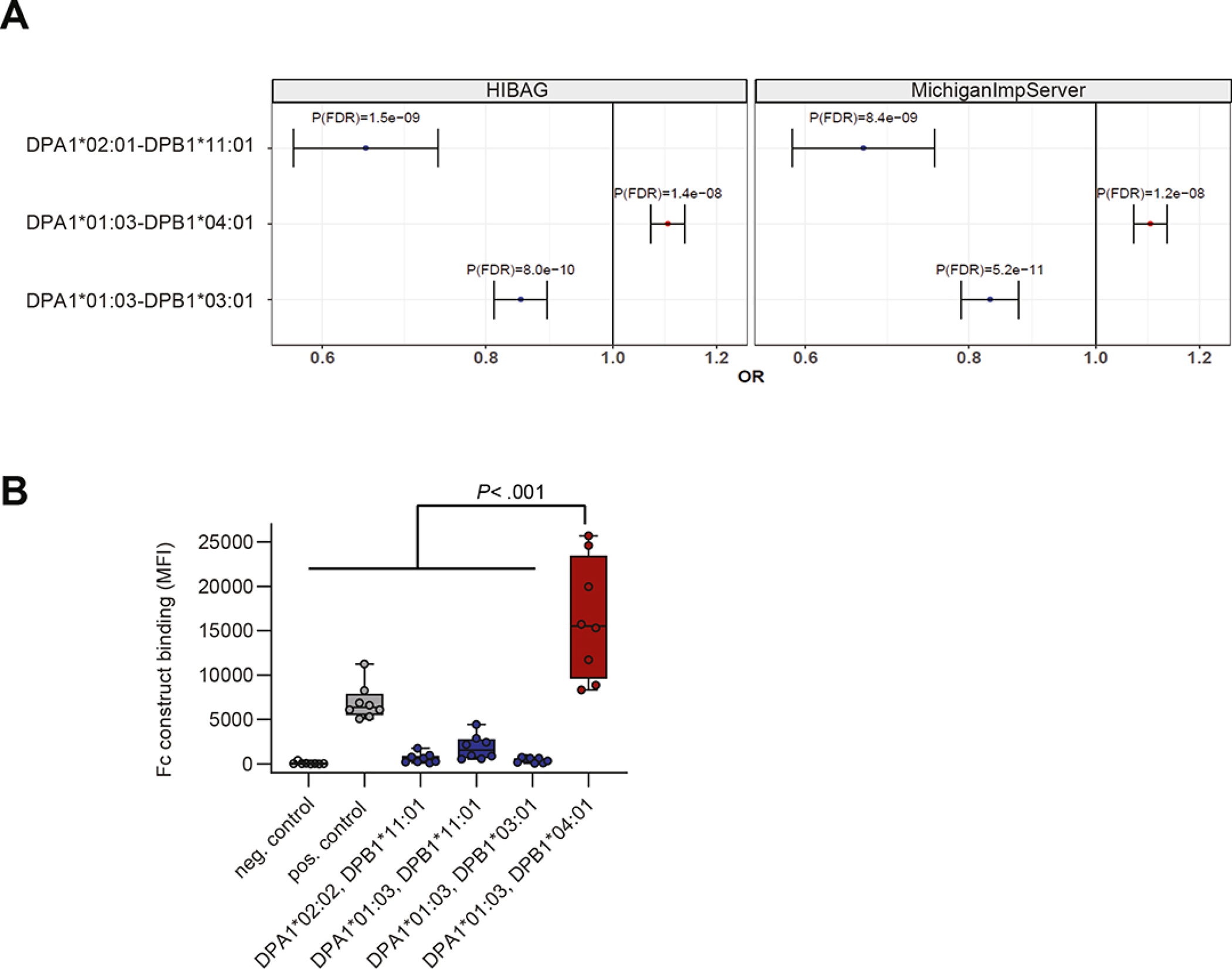
A. Imputation of HLA-DPA1-DPB1 genotypes using HIBAG (left) and MichiganImpServer (right) showing UC risk and protective HLA-DPA1-DPB1 haplotypes with a frequency of >1% and a False Discovery Rate P (P(FDR)) of < .05. Odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals are shown. B. NKp44 Fc construct binding to beads coated with different HLA-DP molecules was determined and medians of fluorescence intensity (MFIs) of all individual experiments (n= 8) are depicted. Boxes indicate medians with 25% and 75% quartile ranges, and whiskers indicate minimum and maximum MFI of each HLA-DP molecule tested. HLA-DP molecules that exhibited higher median binding to the NKp44 Fc construct than to the positive control (IgG-coated beads) are marked in red and less in blue. Statistical significance was measured using Mann-Whitney U comparisons.
