Figure 3. Selection on phototransduction genes.
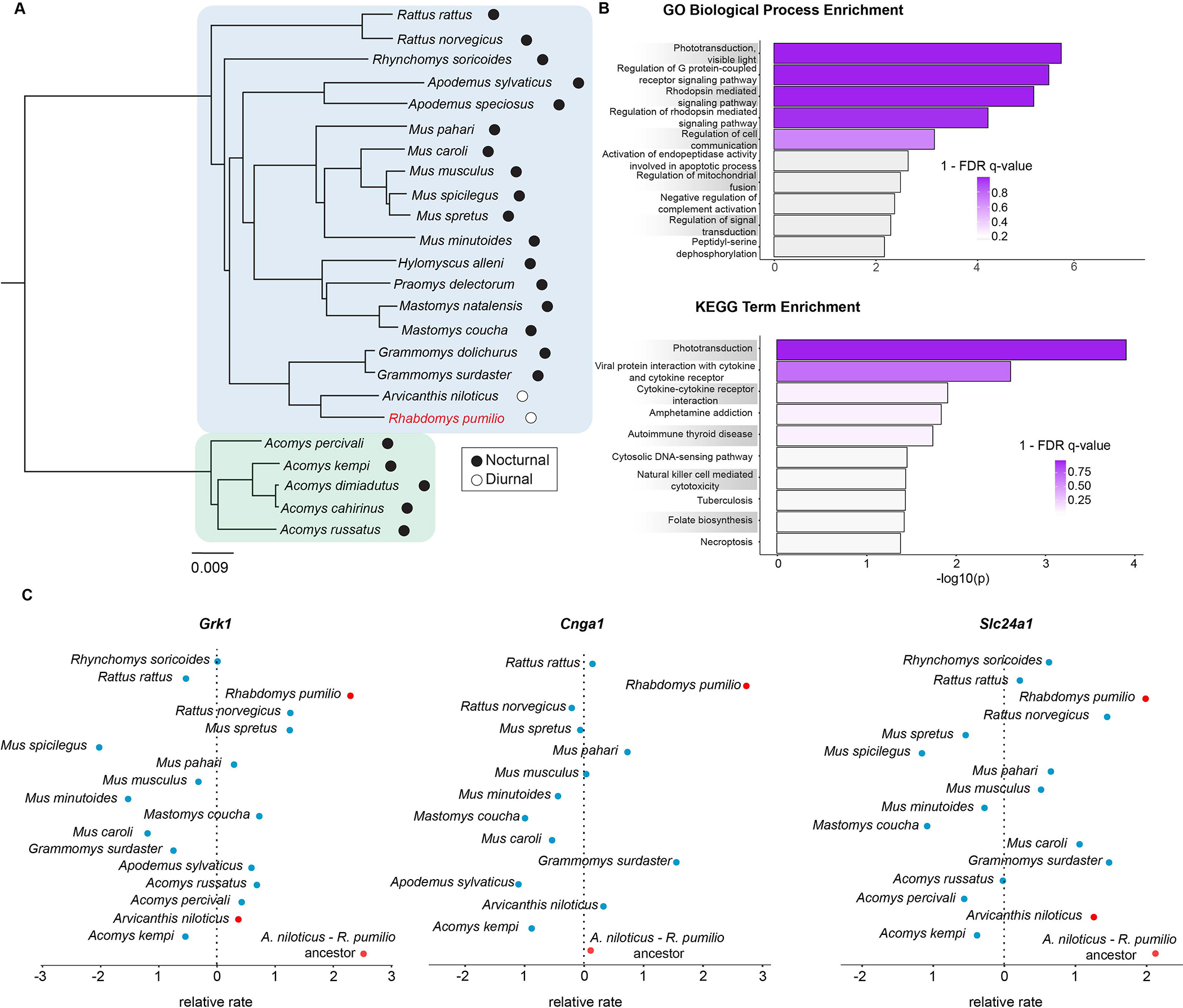
(A) A phylogeny of species used in comparative genomic analyses. Blue colour indicates the subfamily Murinae to which the striped mouse (red font) belongs. Green colour indicates the genus Acomys (subfamily Deomyinae) which served as an outgroup. (B) Enrichment of Gene Ontology Biological Process and KEGG pathway terms among striped mouse genes showing the greatest evolutionary acceleration relative to the background rate. Striped mouse accelerated genes are highly enriched for functions related to phototransduction, particularly those related to the rhodopsin cascade. Colour indicates FDR q-value. (C) Plots showing the relative evolutionary rates (RERs) of three core genes involved in rhodopsin-mediated phototransduction: Rhodopsin Kinase (Grk1), Cyclic Nucleotide Gated Channel Subunit Alpha 1 (Cnga1), and Solute Carrier Family 24 Member 1 (Slc24a1). Compared to closely related murids (blue), phototransduction locus orthologs in the striped mouse (red) show a markedly elevated evolutionary rate.
See also Figures S3, S4 and Data S1C–J.
