Fig. 6. A novel p62-ZZ ligand, YTK-2205 administration reduces fat pad size without loss of muscle.
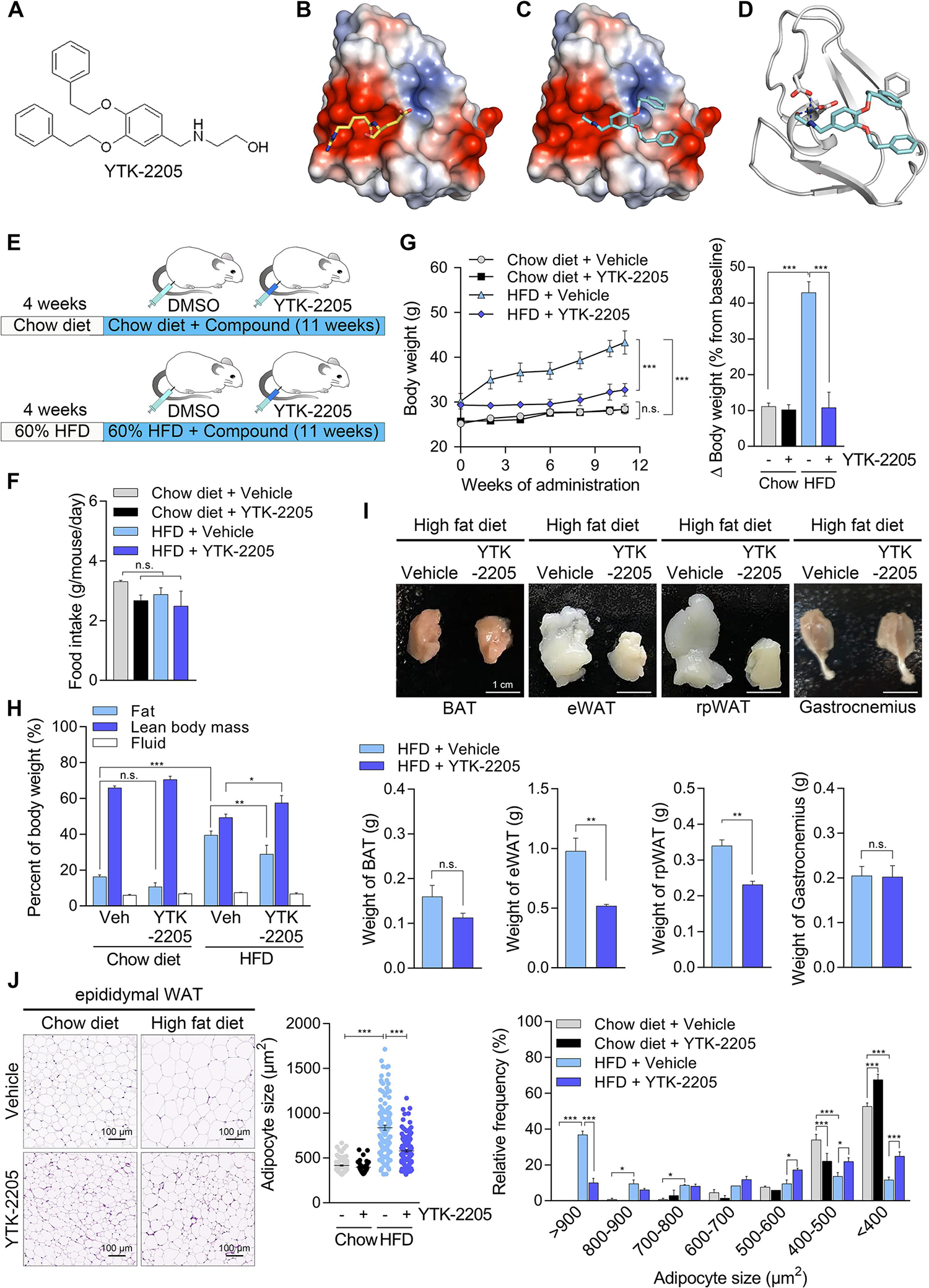
(A) Chemical structure of YTK-2205. (B and C) Docking analysis of YTK-2205 with p62. (D) 3D binding modes and interaction of YTK-2205 with p62. (E) Scheme of YTK-2205 injection in high fat diet (HFD)-induced overweight murine model. (F) Food intake during compound administration (n = 8). (G) Body weight changes during compound administration (left panel, n = 8). Percent body weight changes compared with baseline at the time of sacrifice (right panel, n = 8). (H) Body composition measured by TD-NMR after 11 weeks of compound administration (n = 8). (I) Gross morphology (upper panel) and organ weights (lower panel) of fat pads and gastrocnemius muscle after 11 weeks of compound administration (n = 8). BAT, brown adipose tissue; eWAT, epididymal white adipose tissue; rpWAT, retroperitoneal white adipose tissue. (J) H & E stained eWAT (left panel) and quantification of adipocyte size (middle and right panels, n = 50) treated with YTK-2205 or vehicle. Scale bar, 100 μm. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, n.s., not significant.
