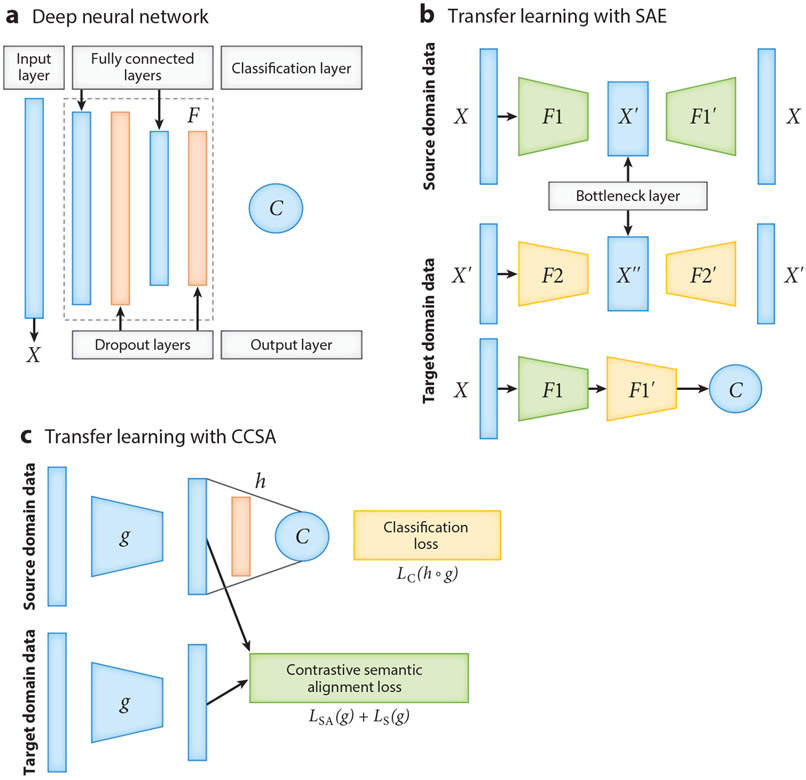
Figure 5.
The neural network architectures for deep learning and deep transfer learning. (a) An example architecture of a deep neural network model, which includes an input layer; several hidden layers (marked as ), including fully connected layers and dropout layers; and one output layer . More fully connected layers can be added to the deep neural network model. (b) The neural network architecture of a stacked denoising auto-encoder (SAE) for transfer learning. (or ) is the encoder with two layers, including a fully connected layer and a dropout layer; (or ) is the decoder; the first and the second rows provide the structure of the first and second auto-encoders, respectively; and is a regression or classification layer. (c) The neural network architecture of classification and contrastive semantic alignment (CCSA) (105). CCSA minimizes the loss function , where represents the composition of a function that maps the input data to an embedding space and a function used to predict the output label from ; is a classification layer; is the classification loss; is the semantic alignment loss; is the separation loss; and is the weight used to balance the classification loss versus the contrastive semantic alignment loss .