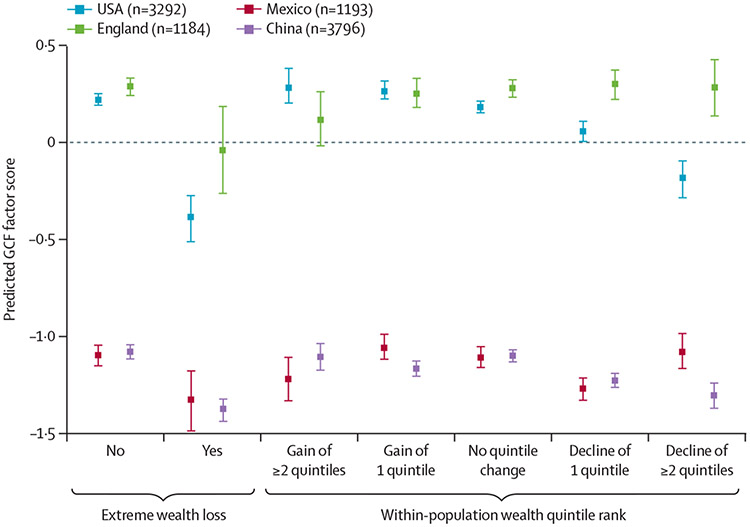
Figure 3: Predicted general cognitive function factor scores following negative wealth shock by country.
The predicted GCF scores were based on the pooled models adjusted for age, age squared, sex or gender, marital status, minority status, household size, participant’s and parents’ education level, baseline wealth quintile, smoking status, BMI, self-reported diagnosed health conditions, self-reported general health, positive for depressive symptoms, and baseline memory score quartile, and accounted for survey sampling weights and household clusters. The predicted GCF scores were calculated by holding the covariates at the mean value within each category of negative wealth shock in each study. Individuals who experienced an increase or decrease in two or more quintile ranks were categorised into one group for prediction due to small sample size. An extreme wealth loss is a 75% or greater decline from the baseline amount of household wealth. The error bars show the 95% CIs of the point estimates, which use standard errors adjusted for household clusters, country strata, and sampling weights. GCF=general cognitive function.