Figure 2. Genetic interactions between ddm1 and histone H3 variants and chaperones impact DNA methylation.
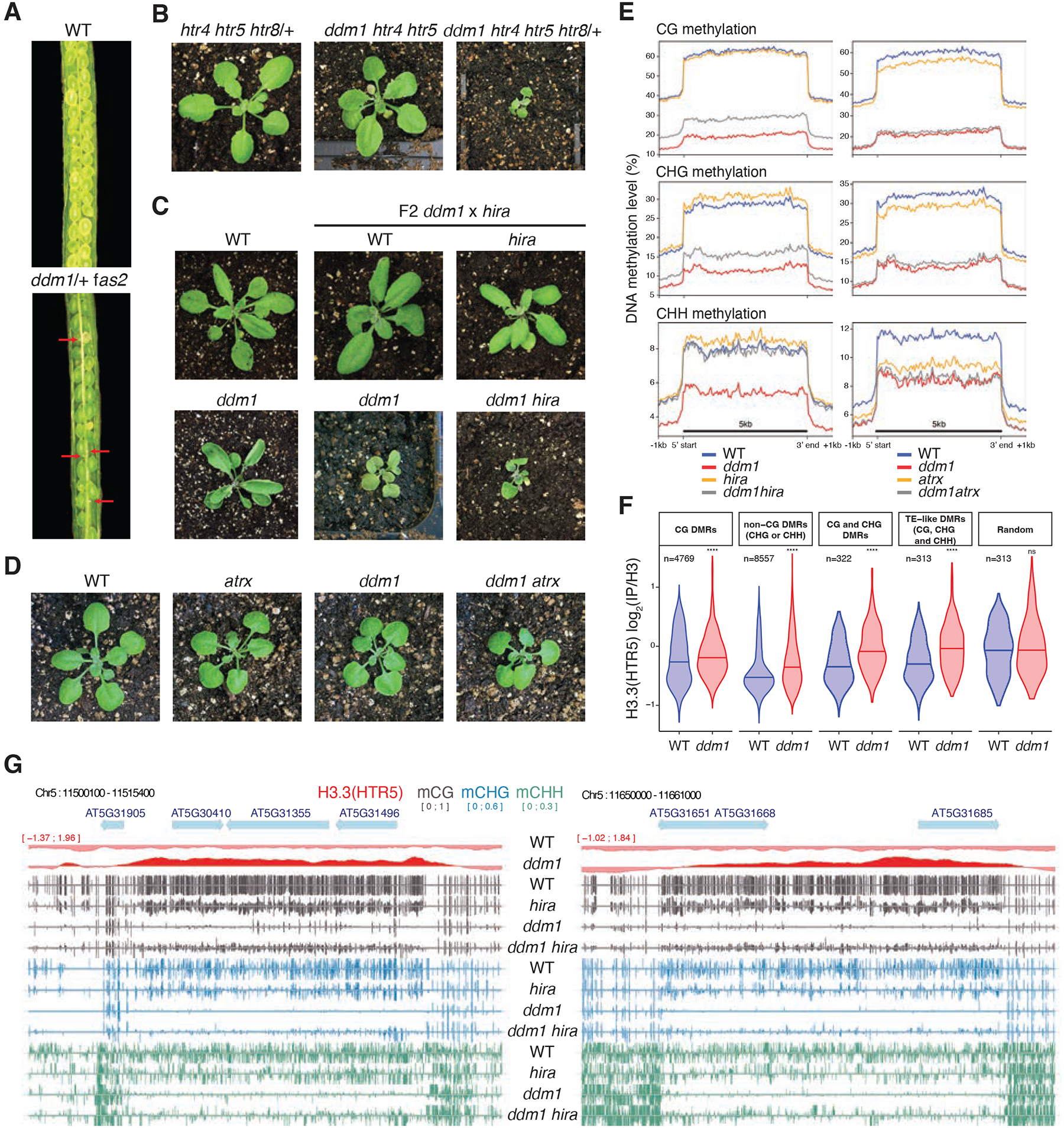
fas2 and hira are mutants in H3.1 (CAF-1), and H3.3 (HIRA) chaperones, respectively. ATRX is a chromatin remodeler required for H3.3 deposition. (A) Siliques of wild-type (WT) and ddm1/+ fas2 plants. Red arrows indicate nonviable seeds (synthetic lethality). (B) F2 ddm1 htr4 htr5 htr8/+ with reduced H3.3 has severe growth phenotypes compared to htr4 htr5 htr8/+. (C) F2 ddm1 hira double mutants from ddm1 and hira parents, compared with WT, hira and ddm1 siblings. (D) F2 ddm1 atrx double mutants from ddm1 and atrx parents compared with WT and ddm1 siblings. ddm1 hira and ddm1 atrx were phenotypically indistinguishable from ddm1 siblings but ddm1 hira were more severe. (E) DNA methylation levels in CG, CHG and CHH contexts in ddm1 and hira mutants on the left, and ddm1 and atrx mutants on the right, determined by whole genome bisulfite sequencing. The DNA methylation levels range from 0 to 100% and are substantially increased in ddm1 hira as compared to ddm1. atrx mutants lose some methylation and fail to rescue methylation loss in ddm1. Metaplots calculated from all 31,189 transposable elements annotated in TAIR10. (F) Levels of H3.3 in WT and ddm1 Chip-seq at differentially methylated regions (DMRs) between ddm1 and ddm1 hira (hyper-methylated in ddm1 hira). The number of DMRs (n) in the different cytosine nucleotide contexts are noted. H3.3 is statistically enriched in ddm1 compared to WT at these DMRs, but not in random regions (**** P<0.0001, ns not significant, t-test). See Table S1 for the list of all DMRs. (G) Representative loci that re-gain DNA methylation in ddm1 hira as compared to ddm1. Ectopic H3.3 in ddm1 is shown above (red track).
