Extended Data Figure 1 |. Engineering and purification of the RXFP1–Gs complex.
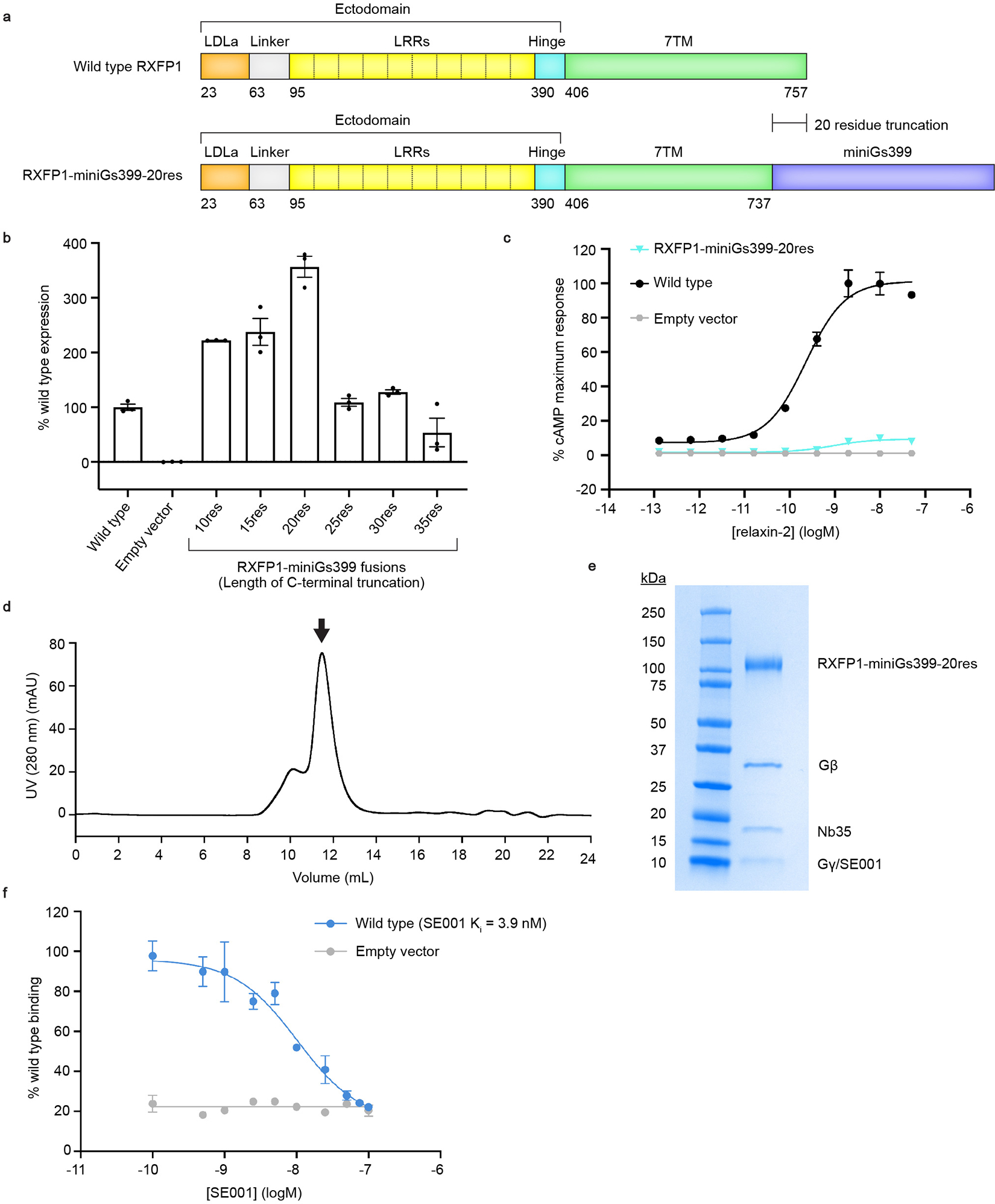
a, Diagram of the primary structure of RXFP1 domains versus the RXFP1-miniGs399–20res fusion construct. b, Flow cytometry cell surface expression tests in Expi293F tetR cells for RXFP1-miniGs fusion constructs. Data is mean ± s.e.m., n = 3 technical replicates. c, Gs signaling assay comparing the signaling levels of wild type RXFP1 versus RXFP1-miniGs399–20res in response to relaxin-2. Data is mean ± s.e.m., n = 3 technical replicates. d, Size exclusion chromatography profile for the RXFP1–Gs complex. Arrow indicates the peak fractions pooled for RXFP1–Gs. e, Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gel for the RXFP1–Gs complex (Representative from 8 purification gels). f, Flow cytometry competition binding assay for SE00111. SE001 competes with 200 nM SE301 for binding to wild type RXFP1. The Ki for SE001 was calculated to be 3.9 nM; data is mean ± s.e.m., n = 3 technical replicates.
