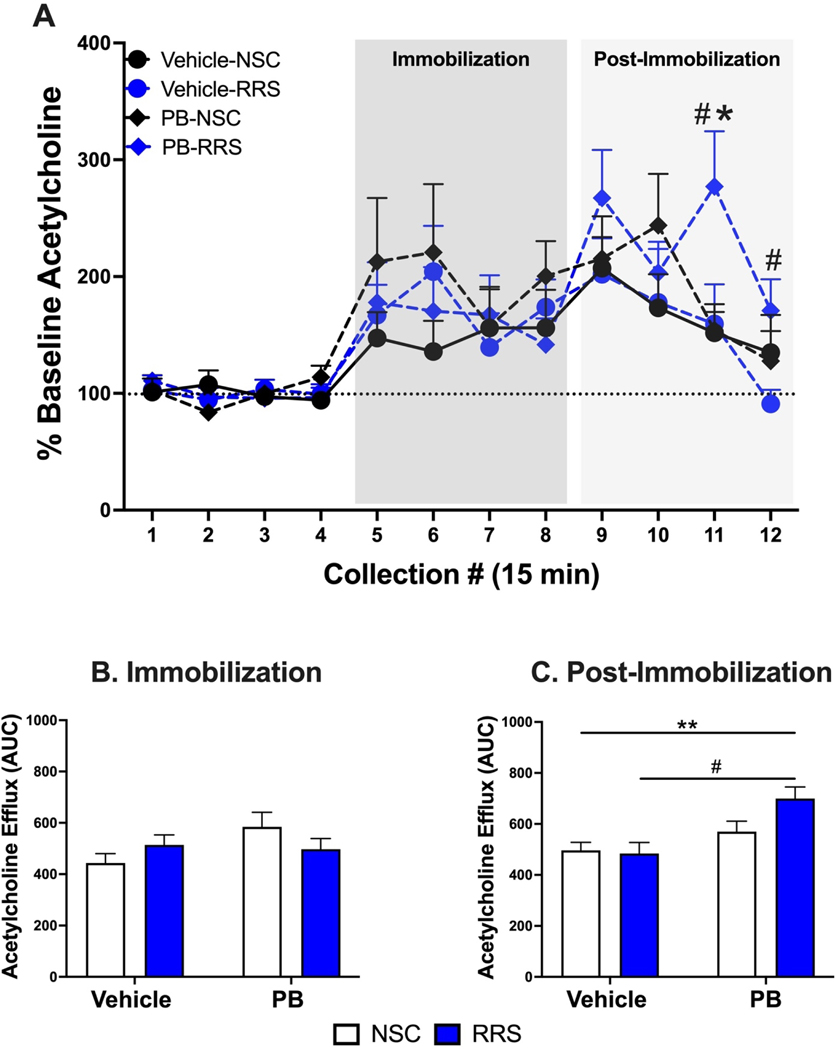
Figure 3: Hippocampal cholinergic responses to immobilization stress 3 months after treatment cessation.
Within rats previously subjected to RRS, a history of PB treatment potentiates the cholinergic response to immobilization stress during the 1-hour recovery period (collections 11 and 12) compared to Vehicle-RRS rats (Panel A). This potentiated response in PB-RRS rats at collection 11 is also significantly greater than the responses of PB-NSC rats. Area under the curve analysis revealed that hippocampal acetylcholine efflux during the 1-hour immobilization stress does not differ between groups (Panel B). However, prior history of PB treatment produces significant elevations in hippocampal acetylcholine efflux in the 1-hour post-stress recovery period (Panel C). All data are expressed as mean + SEM, n = 5–7/group. [#: Significant effect of PB in RRS rats, p < 0.05. *: Significant effect of RRS in PB-treated rats, p <0.05. **: Significant effect of PB, p < 0.01].