Fig. 3. UrIg evolves conservatively among different cartilaginous fish.
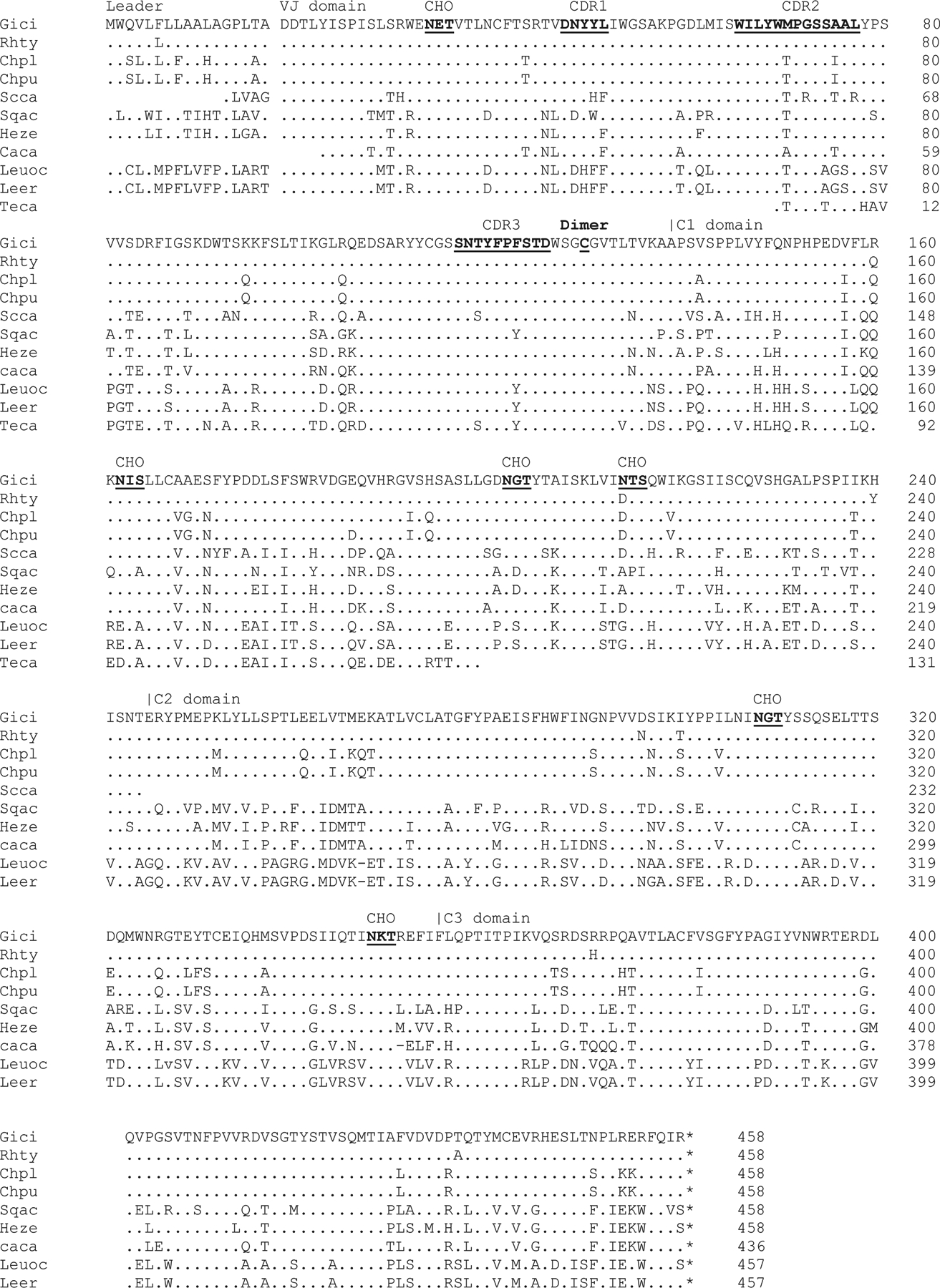
We identified cartilaginous fish UrIg from various databases. Although most of them are gene models (i.e., predicted genes), Clustal omega multiple sequence alignment (ebi.ac.uk) revealed high conservation to the nurse shark UrIg transcripts. Dashes and dots indicate absence and identical amino acid sequences compared to nurse shark UrIg, respectively. CDR, glycosylation sites, and cys-113 are underlined. Species abbreviation and accession numbers, when available)are: Leer: Little Skate: Leucoraja erinacea (JAMYXN010000071.1)*; Teca: Pacific electric ray: Tetronarce californica (GFBV01010368); Leuoc: Winter skate: Leucoraja ocellata (GEZH01007499+GEZH01041997); Sqac: spiny dogfish: Squalus acanthias (HAGU01063221.1); Caca: Great white shark: Carcharodon carcharias (NC_054485.1)*; Heze: Zebra bullhead shark: Heterodontus zebra (GGGL01499922.1)l Scca: small-spotted catshark Scyliorhinus canicula (NC_052158+CACTIS020018579)*; Rhty: Whale shark: Rhincodon typus (XP_048472529.1); Gici: Nurse shark: Ginglymostoma cirratum (GIWU01140354.1; GIWU01140356.1); Chpu: Brownbanded bamboo shark: Chiloscyllium punctatum (BEZZ01003013); Chpl: Whitespotted bamboo shark: Chiloscyllium plagiosum (GCC18650.1). Note that sequences with * indicate were manually curated from the genome assembly and/or transcripts databases.
