Figure 7: Proposed model.
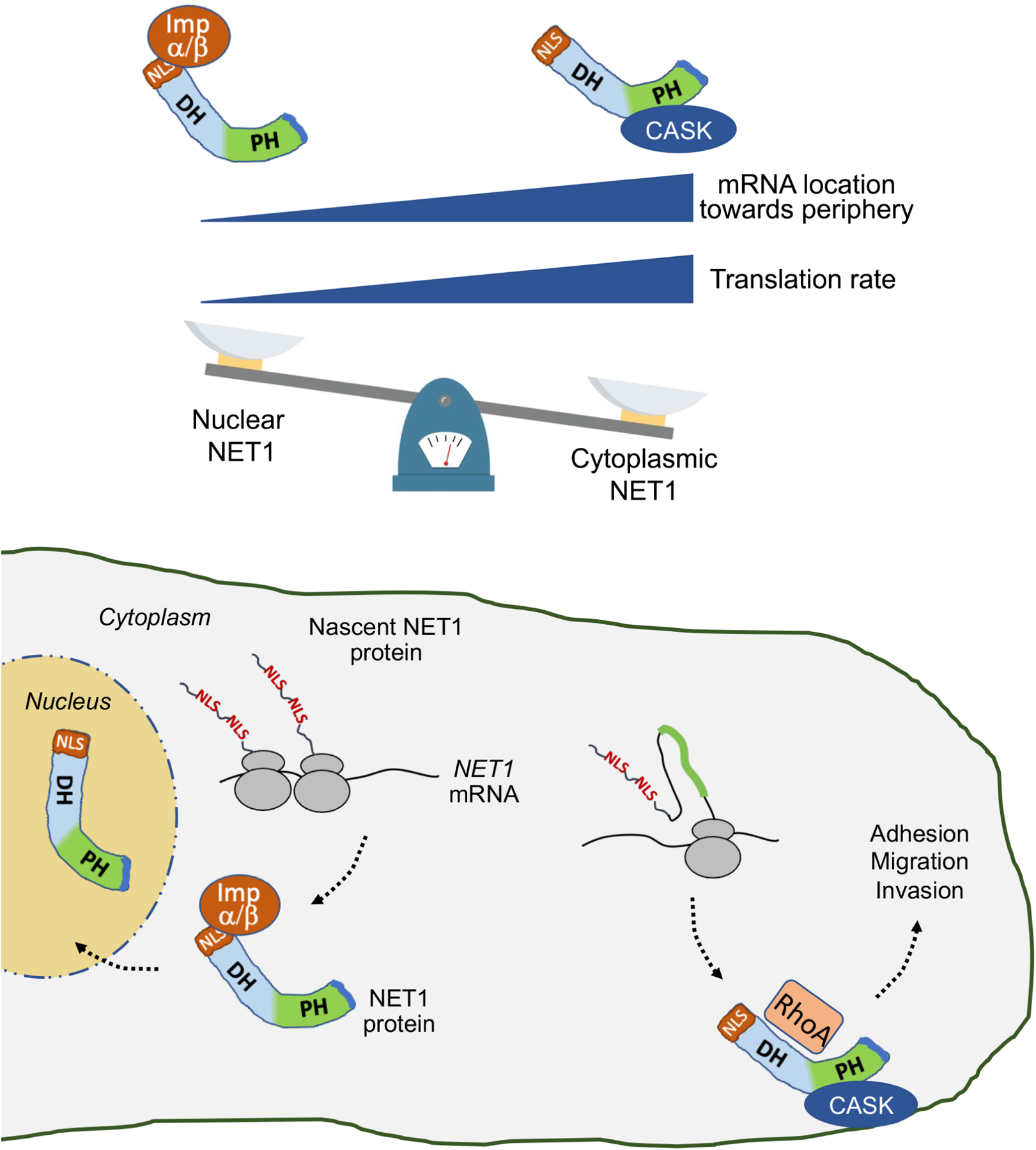
Binding of NET1 to importins or to CASK, and NET1 targeting to the nucleus or cytoplasm, is determined by the location of the NET1 mRNA and the rate of its translation. Perinuclear mRNA and/or slower translation rate favor interaction of the N-terminal NLSs with import receptors and targeting to the nucleus. Peripheral mRNA and/or faster translation rate favor CASK binding through the PH domain to competitively retain NET1 in the cytoplasm. Cytoplasmic NET1 can activate RhoA and promote cell adhesion and migration.
