Figure 1.
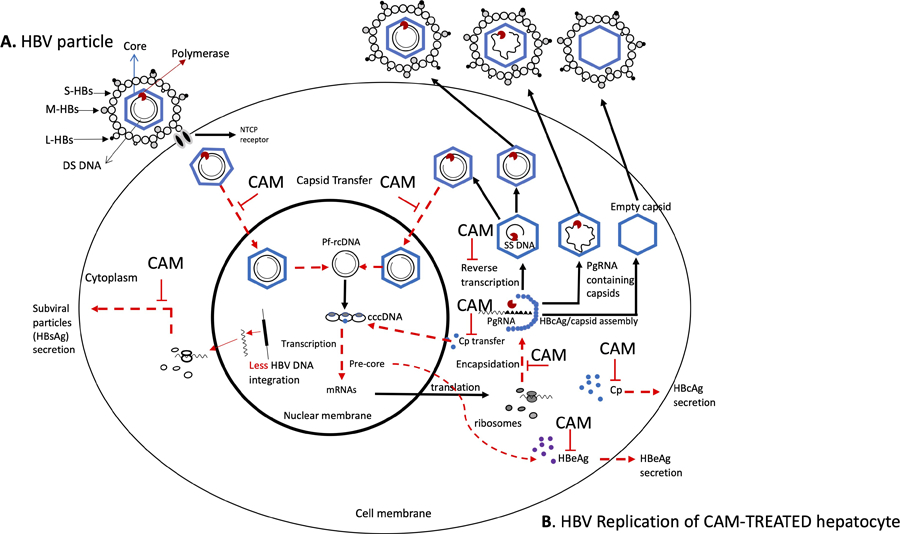
(A & B). HBV replication mechanism and schematic representation of CAM-modulations sites. Panel A represents the HBV particle, and panel B represents the different steps of the HBV replication being affected by CAMs. The dotted arrows in red represent the effects of CAMs on (i) the nuclear transfer of relaxed circular (RC) DNA containing nucleocapsid for covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) synthesis and cccDNA recycling/amplification, (ii) core protein (Cp) secretion on plasma or cytoplasm for nucleocapsid assembly, and nuclear transfer for cccDNA formation, (iii) capsid assembly for pre-genomic RNA (pgRNA) encapsidation, (iv) inhibition of reverse transcription to single-stranded (SS) DNA, (v) HBeAg secretion, and (vi) exposure of HBV DNA for integration in the host genome with low levels of HBsAg production. S, small, M, medium, L, large hepatitis B surface (HBs); DS, double stranded; NTCP, sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide; CAM, capsid assembly modulator.
