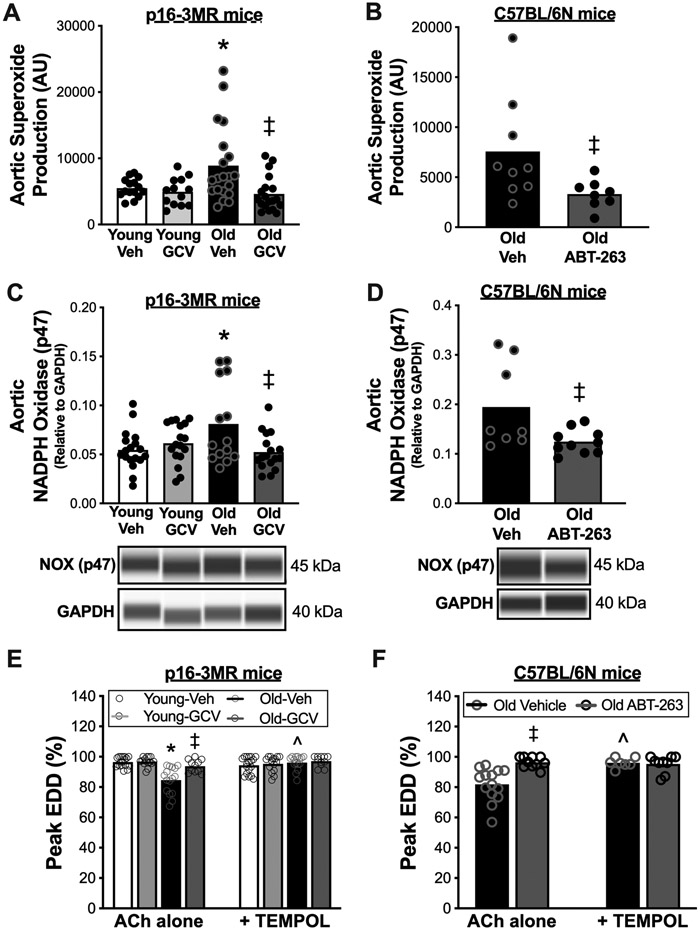
Figure 4. Cellular senescence promotes vascular superoxide-related oxidative stress with aging and senolytic treatment lowers vascular superoxide-related oxidative stress in advanced age.
In young (6-8 months) and old (27-29 months) male and female (sexes combined) p16-3MR mice treated with vehicle (Veh; sterile saline) or ganciclovir (GCV, in sterile saline) at a dose of 25 mg/kg/day for five consecutive days via intraperitoneal injection: (A) Aortic superoxide production (electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy amplitude units [AU]). (C) Aortic abundance of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAPDH) oxidase p47 normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). (E) Peak carotid artery endothelium dependent dilation (EDD) to acetylcholine (ACh) with vs. without the presence of the superoxide dismutase mimetic TEMPOL. In old male C57BL/6N mice treated with vehicle (10% ethanol; 30% PEG400; 60% Phosal 50PG) or ABT-263 (in the vehicle) at a dose of 50 mg/kg/day via oral gavage following a one week on – two weeks off – one week on dosing regimen: (B) Aortic superoxide production (electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy, AU). (D) Aortic abundance of NAPDH oxidase p47 normalized to GAPDH. (F) Peak carotid artery EDD to ACh with vs. without the presence of TEMPOL. All data are mean ± SEM. N = 15-20/group, p16-3MR mice aortic superoxide production, and aortic NAPDH oxidase p47 and CuZn SOD abundance. N = 10-15/group, p16-3MR mice peak EDD with TEMPOL. N = 8-9/group, ABT-263 study aortic superoxide production. N = 8-10/group, ABT-263 study aortic NADPH oxidase p47 abundance. N = 10-12/group, ABT-263 study aortic CuZn SOD abundance. N = 7-9/group, ABT-263 study peak EDD with TEMPOL. * P < 0.05, effect of aging within group; ‡ P < 0.05, effect of treatment within age group; ^ P < 0.05, ACh alone vs. ACh + TEMPOL.