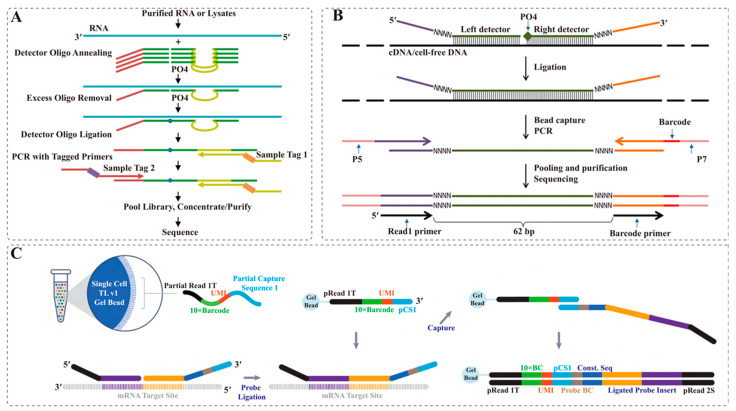
Figure 2.
sc/snRNA-seq of FFPE samples based on gene probe capture techniques. (A) TempO-Seq biochemical LOSscheme. Reprinted with permission from ref. [37]. Copyright 2017 PLOS ONE. RNAs are targeted by annealing to DOs that contain target-specific sequences (green), as well as primer landing sites (red and yellow) that are shared across all Dos; Excess oligos are removed by a 30 exonuclease, then the hybridized oligos are ligated and amplified using primers that contain sample tag (index) sequences (orange and purple bars) and adaptors required for sequencing. (B) Schematic diagram of the assay to detect specific mRNA or cell-free DNA. Reprinted with permission from ref. [39]. Copyright 2018 Genomic Medicine. Target-specific DNA oligonucleotide detector probes hybridize under stringent conditions to the studied cDNA or cfDNA; Both detector oligonucleotides consist of a specific 27 bp region (green), 4 bp unique molecular identifier (UMI), and universal sequences (purple and orange); The right detector oligonucleotide is 5′ phosphorylated. After rigorous hybridization, the pair of detector probes is ligated using a thermostable ligase under stringent conditions; Next, the ligated detectors complexed with the target region are captured with magnetic beads and PCR amplified to introduce sample-specific barcodes and other common motifs that are required for single-read NGS. (C) Chromium Single-Cell Fixed-RNA Profiling library construction principle. Cells are fixed and permeabilized; Samples are hybridized to probe sets and may be processed individually or pooled with up to 16 samples in a single lane of a Chromium chip; During GEM generation, the probe sets are ligated and extended to incorporate unique barcodes. Sequencing libraries are then prepared, sequenced, and analyzed.