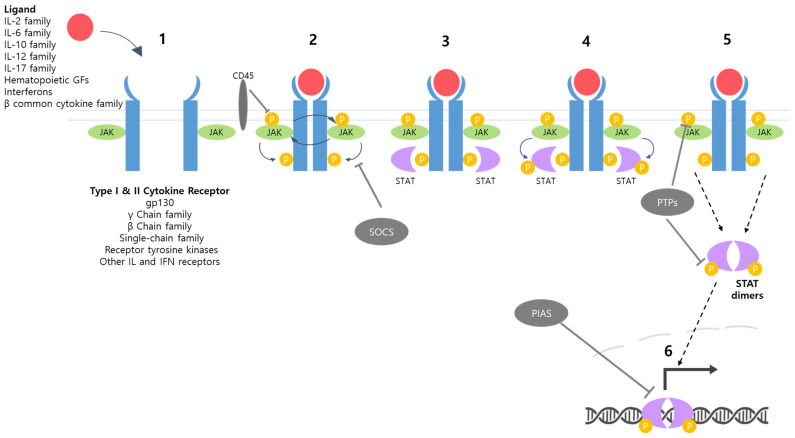
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Ligand binding to cytokine receptor leads to the formation of receptor dimerization (1). The dimerization induces the transphosphorylation of JAK as well as phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic tails of the receptors (2). STAT binds to the phosphorylated site of the receptor (3). Subsequently, JAK phosphorylates STAT recruited to the receptors (4). Phosphorylated STATs dissociate from the receptors and form a dimer (5). STAT dimers translocate into the nucleus and induce the transcription of target genes (6). There are three types of negative regulators of the JAK/STAT signaling: suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS), inhibiting the phosphorylation of the receptor by JAK; protein inhibitors of activated STAT (PIAS), preventing the activity of STAT transcription factors; and protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs), removing phosphate groups from JAKs and STATs.