FIGURE 3.
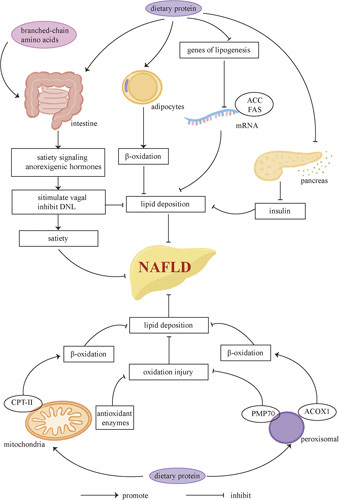
Protein and NAFLD. Dietary protein can help treat NAFLD by promoting satiety and inhibiting lipid deposition. Elevated branched-chain amino acids can stimulate satiety signaling. Anorexigenic hormones can also promote vagal activities and inhibit DNL. What’s more, dietary protein can increase β-oxidation of lipids in adipocytes, suppress the expression of lipogenesis genes, and decrease serum insulin levels, all of which inhibit hepatic lipid deposition. Proteins can also increase the expression of antioxidant enzymes in the mitochondria and PMP70 in the peroxisomes to decrease oxidation injury. The expression of peroxisomal ACOX1 and mitochondrial CPT2, which can increase β-oxidation of lipids, is also increased after supplementing dietary protein. Abbreviations: ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; ACOX1, acyl-CoA oxidase 1; CPT, carnitine palmitoyl transferase; DNL, de novo lipogenesis; PMP70, peroxisomal membrane protein 70.
