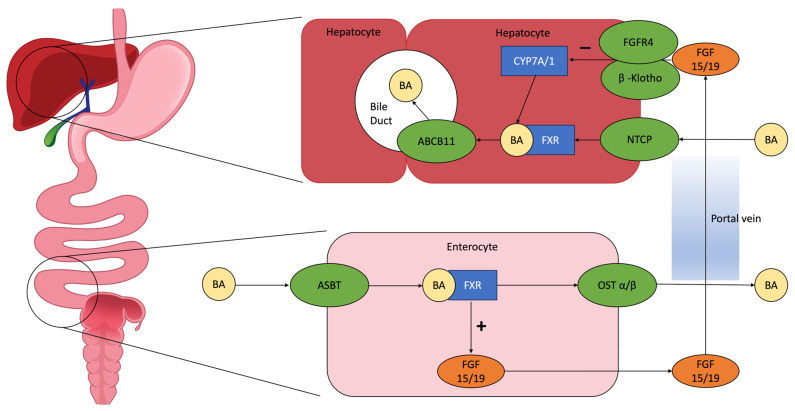
Figure 1.
Pathophysiology of enterohepatic circulation: BAs excreted in the intestinal lumen are mainly reabsorbed in the ileum through the apical sodium-dependent bile acid transporter (ASBT) and return to the liver through the portal circulation, stimulating the farnesoid X receptor (FXR). This initiates the production of fibroblast grow factor (FGF) 15/19, which interacts in the hepatocytes with cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase (CYP7A/1) and reduces BA synthesis, with a negative feedback mechanism [16]. Abbreviations: BA = bile acid; ASBT = apical sodium-dependent bile acid transporter; FXR = farnesoid X receptor; FGF 15/19 = fibroblast grow factor 15/19; OST α/β = organic soluble transporter α/β; FGFR4 = fibroblast grow factor receptor 4; CYP7A/1 = cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase; NTCP = sodium-dependent uptake transporter; ABCB11 = ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 11.