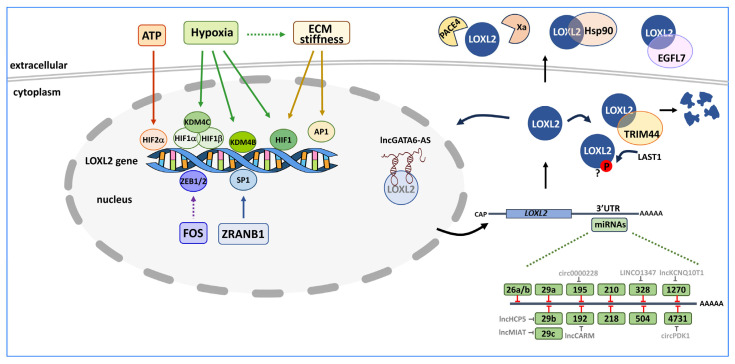
Figure 3.
LOXL2 regulation. Left side, LOXL2 gene expression is regulated in different cancer scenarios by three well characterised signalling pathways (extracellular ATP, hypoxia, and ECM remodelling) that impinge on different transcriptional factors, including HIF1α, HIF1β, HIF2α, and lysine demethylases KDM4B and KDM4C. The proto-oncogene c-FOS controls LOXL2 expression through the Wnt7/9-ZEB1/2 axis. Deubiquitinase ZRANB1 stabilises the transcription factor SP1. Right bottom cytoplasm side, several miRNAs act through the LOXL2 3’UTR mRNA region to downregulate its gene expression. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNA) and circular RNAs (circRNA) counteracting the miRNAs (green boxes) are marked in grey. Right upper cytoplasm side, LOXL2 is directed to the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway by the interaction with TRIM44. LOXL2 is phosphorylated by LAST1 with unknown functional consequences. Upper right side, LOXL2 in the extracellular compartment undergoes proteolytic processing by PACE4 and factor Xa proteases, and secreted EGFL7 inhibits LOXL2 catalytic activity. Extracellular LOXL2 also interacts with HSP90, although the functional consequences of this interaction are unknown. Nuclear LOXL2 is negatively regulated by the lncRNA GATA6-AS. The question mark (?) means that the functional consequences of LOXL2 phosphorylation are unknown.