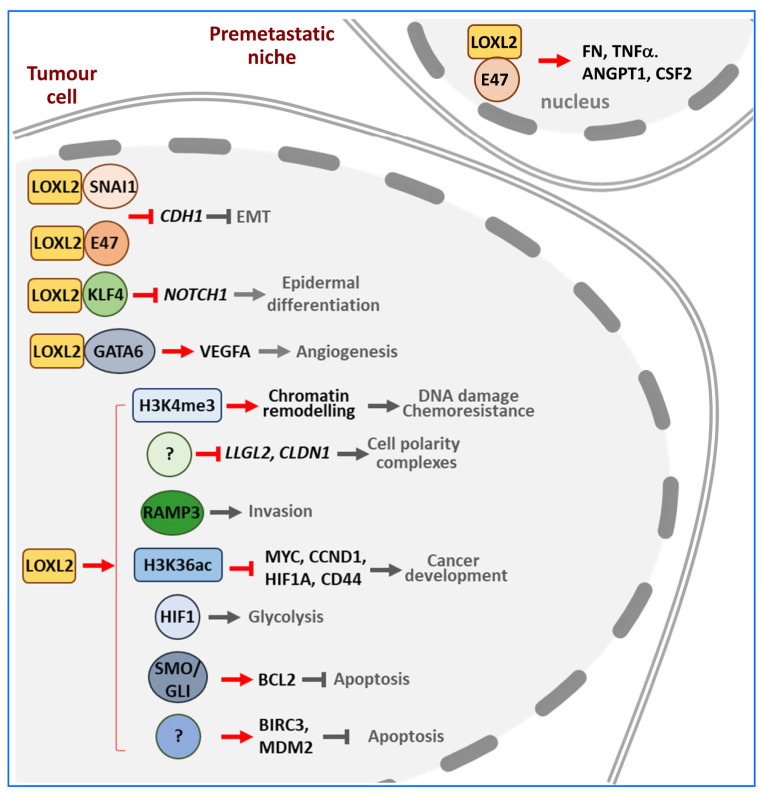
Figure 6.
Nuclear targets of LOXL2. In different tumour scenarios, nuclear LOXL2 exerts its pro-tumorigenic roles by interacting with various transcription factors (SNAI1, E47, KLF4 and GATA6), modifying histone marks (H3K4me3 and H3K36ac), and upregulating the expression of different effectors (HIF1, SMO/GLI, and RAMP3). The downregulation of cell polarity complex genes (LLGL2, CLDN1) and upregulation of antiapoptotic genes (BIRC3 and MDM2) are mediated by unknown transcription factors. Red arrows denote positive regulation and red blunt-end arrows signify negative regulation exerted by LOXL2 on the indicated targets. Final functional processes altered by LOXL2 action are marked in grey. The question mark (?) means that the direct LOXL2 target or the functional consequences of an LOXL2 action are unknown.