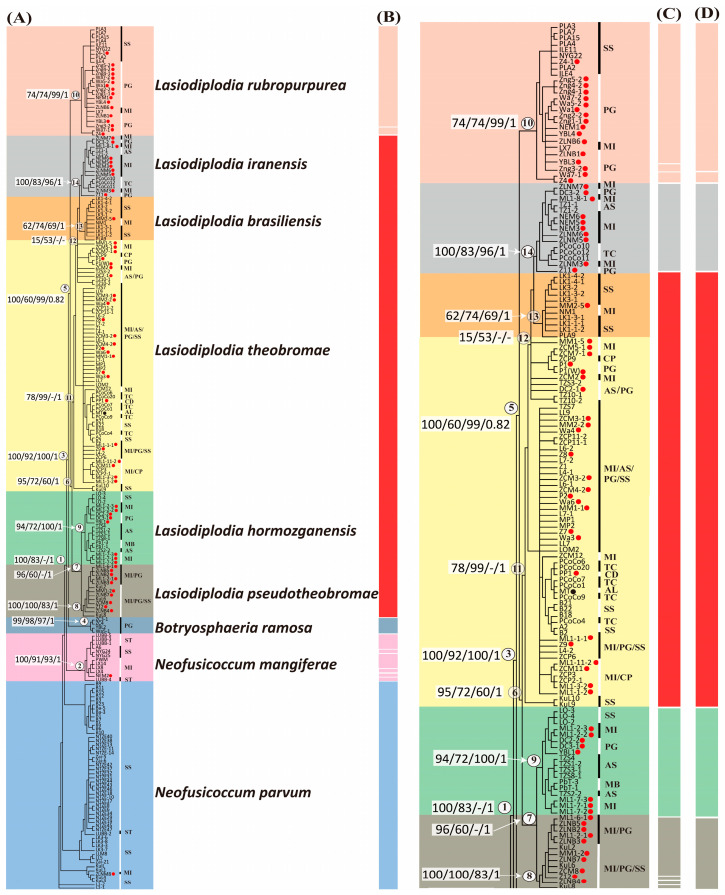
Figure 4.
(A) The Phylogenetic tree was constructed using Maximum Parsimony of the Lasiodiplodia and Neofusicoccum species isolated from different fruit species in Taiwan based on DNA sequence data for four loci (SSU, ITS, TEF1, TUB2). Branches were marked with the Maximum Parsimony bootstrap values, Maximum Likelihood bootstrap values, Neighbor-Joining bootstrap values, and Bayesian posterior probabilities, respectively. The red spots indicated that the sample was isolated from the stem. (B) ABGD results included six Lasiodiplodia, two Neofusicoccum, and one Botryosphaeria species. (C) ABGD results, including six Lasiodiplodia species. (D) ASAP results included six Lasiodiplodia species. [The host species codes] SS: Syzygium samarangense (wax apple); PG: Psidium guajava (guava); MI: Mangifera indica (mango); CP: Carica papaya (papaya); AS: Annona squamosa (sugar apple); TC: Theobroma cacao (cocoa); MB: Musa basjoo (banana); CD: Cordia dichotoma; AL: Alpinia; ST: Syzygium taiwanicum. The nodes were labeled with numbers (1–14) encircled by circles.