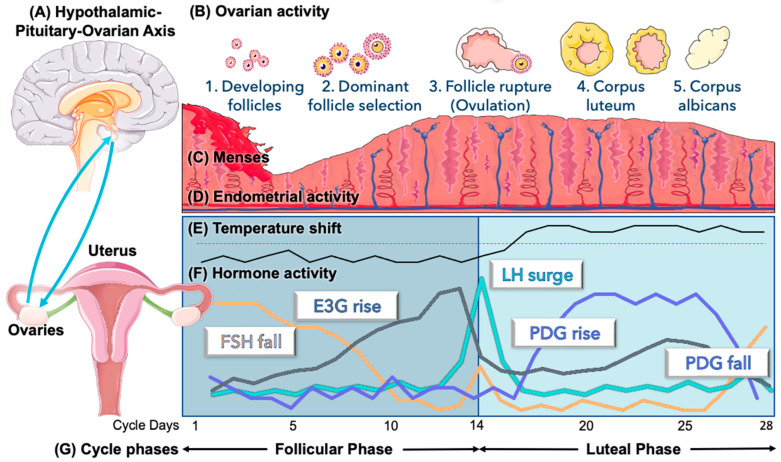
Figure 1.
Ovarian–uterine (menstrual) cycle. (A) The hypothalamic–pituitary–ovarian (HPO) axis involves hormonal feedback loops between the ovaries, the hypothalamus, and the pituitary, which regulate the reproductive hormones and ovulation (B). A cycle begins with menses (C), the shedding of the endometrial lining (D), while follicle development is stimulated by FSH and estrogen (E13G) to select a dominant follicle, which ruptures to release an egg under the stimulation of the LH surge (F). Progesterone rises after ovulation, which causes a basal body temperature shift (E) and supports the lining of the uterus (endometrium, (D)) to facilitate implantation of an embryo. If no embryo implants, progesterone falls (F), leading to menses (C). The follicular phase is from menses until ovulation, and the luteal phase is from ovulation until the end of the cycle (G). Adapted by T. Bouchard with permission from SERVIER Medical Art (smart.servier.com, accessed on 1 October 2022).