Fig. 6. Models for pulmonary ionocyte anion transport function in a multicellular airway epithelium.
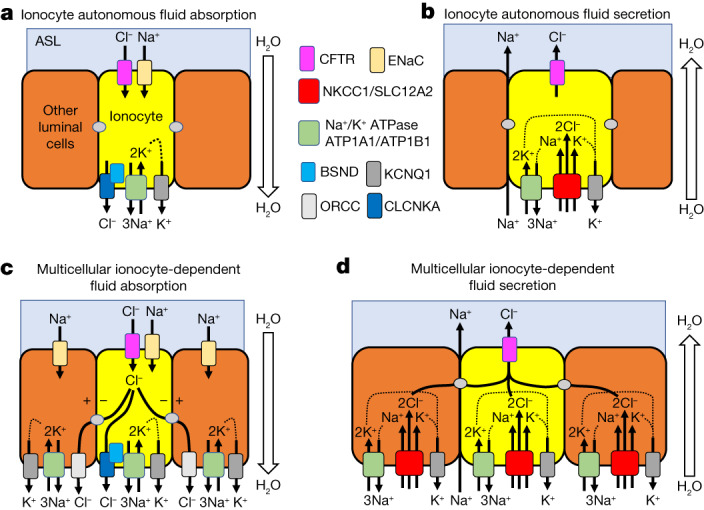
a,b, Pulmonary ionocytes (yellow) function in a cell-autonomous manner to facilitate anion movement across airway epithelia required for fluid absorption (a) and fluid secretion (b). c,d, Multicellular ionocyte-dependent anion movement utilizing electric coupling through gap junctions to facilitate fluid absorption (c) and fluid secretion (d). The second models propose that Na+ and K+ electrical driving forces in cells coupled to ionocytes collectively drive Cl− absorption and secretion through CFTR in pulmonary ionocytes. In both models, the ionocyte channels shown were differentially enriched in the pulmonary ionocyte transcriptome. ORCC, outward rectifying Cl− channel.
