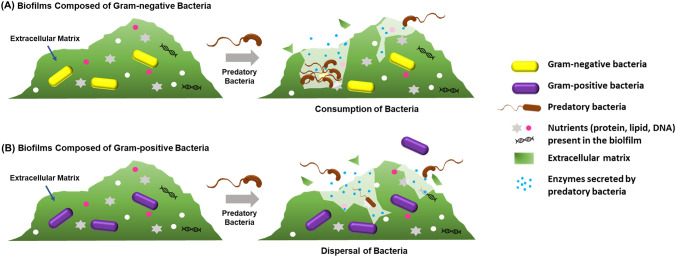
Fig. 2.
Removal of biofilms by intraperiplasmic predatory bacteria. (A) Susceptible Gram-negative bacterial biofilms are consumed by the predator, reducing the viability of the prey present within. (B) In contrast, Gram-positive bacteria are not predated on, meaning their viabilities do not decrease when the predator encounters their biofilms but are rather dispersed as the predator hydrolyzes the extracellular polymeric substances composing the extracellular matrix