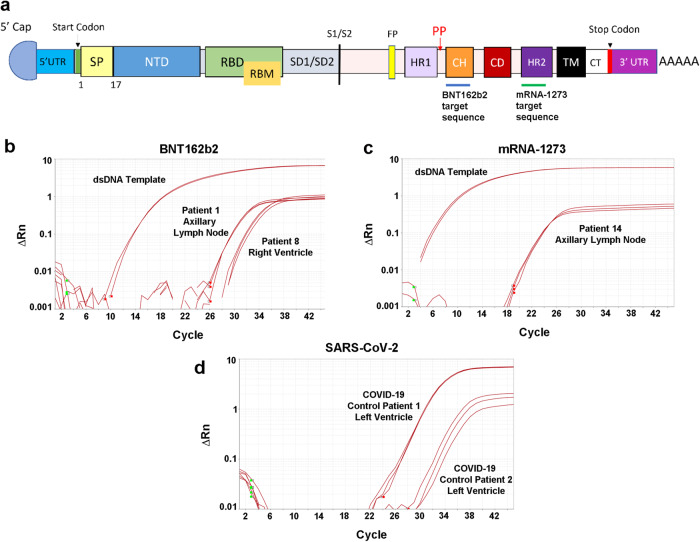
Fig. 1. Screening autopsies for mRNA vaccines with designed RT-qPCR assays.
Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in autopsies requires devising sequence-specific regions for RT-qPCR assays within the spike gene structure. a The functional domains of the mRNA vaccine SARS-CoV-2 spike protein includes the assay targets for the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in the central helix (CH) domain (blue line below). For detection of the mRNA-1273 vaccine (green line), the assay detects a sequence within the heptad repeat 2 (HR2) segment (see Table 2). UTR untranslated region, SP signal peptide, NTD N-terminal domain, RBD receptor-binding domain, RBM receptor-binding motif, SD subdomain, FP fusion peptide, HR1 heptad repeat 1, CD connector domain, TM transmembrane, CT cytoplasmic tail. Also marked is the start codon (green line), stop codon (red line), S1/S2 cleavage site (black line), the vaccines’ two Proline substitutions (red P’s), and the polyA tail at the end. Sample amplification plots of RT-qPCR assays to detect b BNT162b2 and c mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in axillary lymph node autopsy samples. Double-stranded DNA templates (dsDNA) were used as positive controls. d All vaccine-positive samples were further screened for SARS-CoV-2 E gene. The viral gene was detected only in the two SARS-CoV-2 infected cardiac left ventricle samples (positive controls).