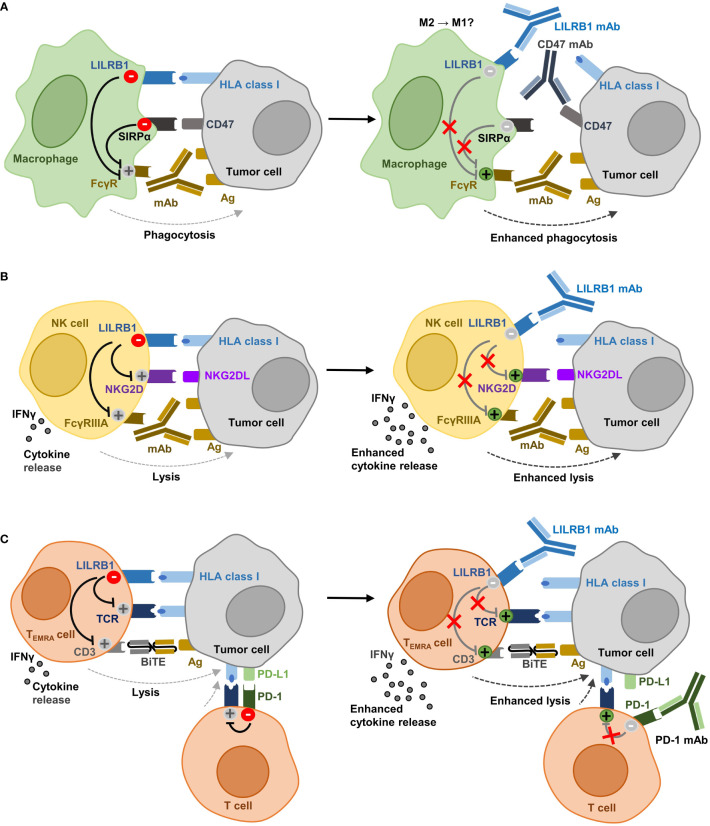
Figure 2.
Potential effector functions of anti-LILRB1 antibodies in cancer immunotherapy. (A) Recognizing HLA class I molecules, LILRB1 functions as an immune checkpoint in macrophages and inhibits together with the CD47 receptor SIRPα phagocytosis of tumor cells. Antagonistic LILRB1 antibodies enhance phagocytosis and promote ADCP by therapeutic antibodies that target an antigen expressed by the tumor and which provide an ‘Eat Me!’ signal by ligation of activating FcγR. LILRB1 blockade also cooperates with CD47 antibodies in enhancing ADCP. Since a role for LILRB1 has been implicated in macrophage polarization, the blockade of the HLA class I:LILRB1 axis may support re-programming of TAM from an M2-like phenotype towards M1. (B) In NK cells, LILRB1 engagement impairs both cytokine release and cytotoxicity. LILRB1 ligation hampers lysis of cancer cells induced by NK cell lysis receptors such as NKG2D or by activation of FcγRIIIA through therapeutic antibodies targeting a tumor-expressed antigen. LILRB1 antibody blockade enhances cytokine release, natural cytotoxicity and ADCC. (C) In CD8-positive T cells, mainly TEMRA cells, LILRB1 inhibits cytokine release and cytotoxic functions triggered by activation of the T cell receptor. LILRB1 ligation also impairs tumor cell lysis induced by therapeutic BiTE molecules specific for a tumor cell expressed antigen and activating CD3. Antagonistic LILRB1 antibodies promote cytokine release and T cell cytotoxicity and may be employed to enhance the efficacy BiTE molecules. The expression of PD-1 and LILRB1 on different T cell subsets renders LILRB1 blockade attractive for combination with anti-PD-1 antibodies to abrogate inhibitory signaling in both T cell populations (Ag, antigen; NKG2D, natural killer group 2 member D; NKG2DL, NKG2D ligand; FcγRIIIA, Fcγ receptor IIIA; TCR, T cell receptor; BiTE, bispecific T cell engager; PD-1, programmed cell death 1; PD-L1, PD-1 ligand 1).