Figure 5.
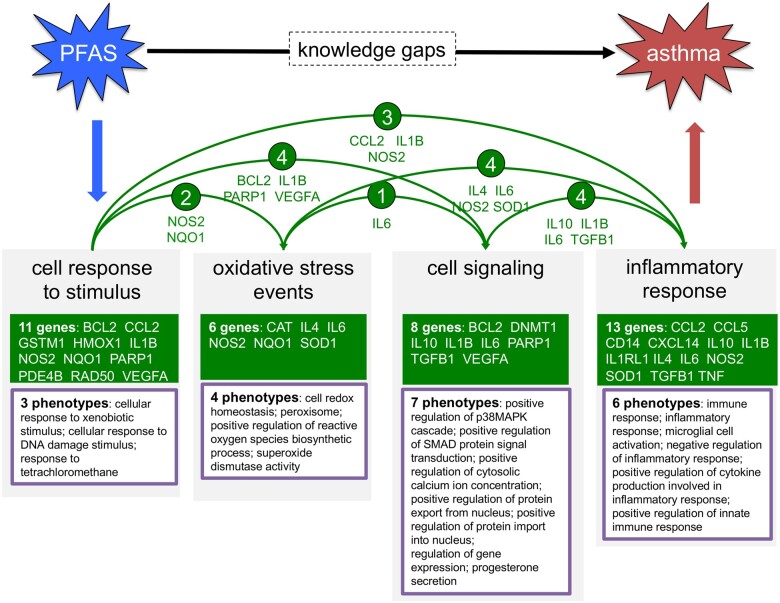
Use case 1: computing mechanistic framework to fill knowledge gaps for PFAS and asthma. The CTD Tetramers tool generated 203 CGPD-tetramers connecting 2 PFAS chemicals to asthma (Supplementary Table 1). Similar phenotypes were manually grouped and binned into modules (Table 2), such as “oxidative stress events” made up of 4 distinct phenotypes. Here, 4 modules are shown (“cell response to stimulus,” “oxidative stress events,” “cell signaling,” and “immune/inflammatory response”), composed of 23 total genes and 20 unique phenotypes. These modules are connected by shared genes (arrows). Importantly, additional modules (eg, “cell death” and “triglyceride metabolism” from Table 2) can be incorporated to further expand the chemical-disease pathway. The computed molecular mechanisms offer potential solutions that fill knowledge gaps between PFAS and asthma.