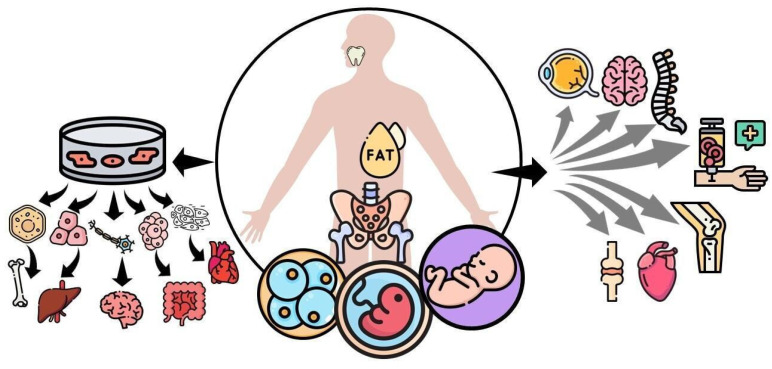
Figure 1.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can be classified based on the developmental stage in which they are extracted, such as embryonic, fetal, infant, or adult mesenchymal stem cells. They can self-renewal and differentiate into various tissues under appropriate in vitro stimulation, including bone, cartilage, muscle, bone marrow stroma, tendon/ligament, fat, and dermis. On the other hand, MSCs that are not subjected to differentiation in vitro are being tested to treat connective tissue disorders, acute myocardial infarction, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, spinal cord injury, osteoarthritis, ocular burns, and graft versus host disease.