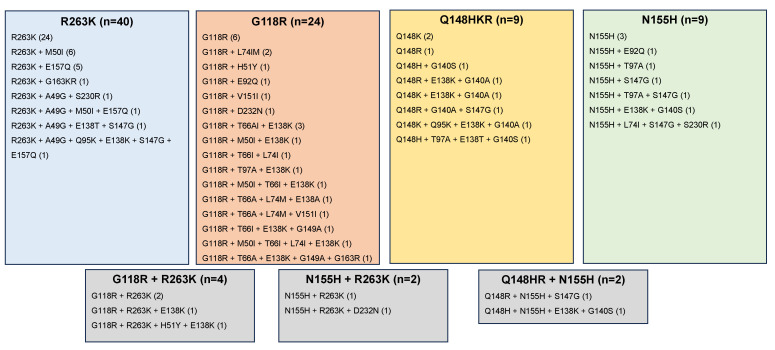
Figure 2.
Patterns of INSTI-associated DRMs occurring in 99 previously INSTI-naïve individuals with virological failure on a DTG-containing regimen who developed a major nonpolymorphic INSTI-associated DRM defined as one of the following mutations: H51Y, T66A/I/K, E92G/Q, G118R, F121Y, E138A/K/T, G140A/C/S, Y143C/H/R/S, S147G, Q148H/R/K, S153Y/F, N155H, S230R, and R263K. Polymorphic and accessory DRMs were identified only when they occurred in an isolate that also contained a major nonpolymorphic INSTI-associated DRM. Additional patterns of mutations that do not conform to the above categories included one with and eight without signature DRMs. The one with signature DRMs included L74I + G118GR + E138K + Q148QR + R263RK. The eight without signature mutations included S230R (n = 3), T66I, E138K, H51Y + S147G, E138A + G149A, and E138K + D232N.